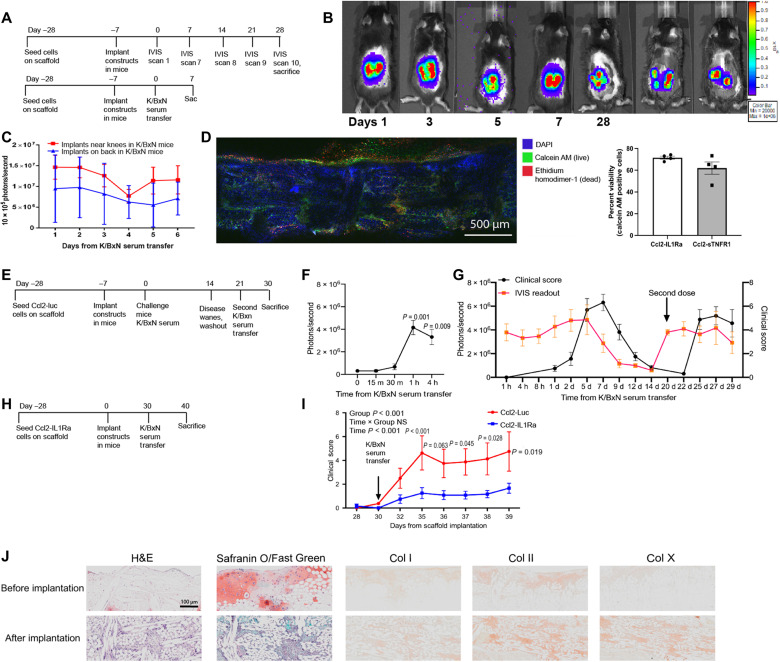
Fig. 4. Bioartificial implants demonstrate translationally relevant longevity, therapeutic efficacy, and retriggering dynamics.
(A and B) When implanted in K/BxN model of RA, Ccl2-Luc implants expressed consistent luciferase and (C) photon flux was similar across subcutaneous implantation on the dorsal aspect or proximal to the knee joint in mice (n = 3 per group). (D) Explanted constructs demonstrated high cell viability via confocal microscopy. (E) Ccl2-Luc implants were delivered to mice and (F) challenged to evaluate the on-dynamics where significant increase in photon flux (photons per second) was observed 1 hour after K/BxN STA. (G) Luciferase signal was measured in concert to clinical score over an initial flare, and after a week-long washout period through which minimal signal was detected in concert with attenuated clinical score. The same mice were triggered with a second K/BxN STA flare where a proportional increase in signal was observed. (H and I) An additional group of mice were treated with therapeutic constructs, which laid dormant in mice for 30 days before K/BxN STA, at which time they successfully mitigated disease severity when compared to Ccl2-Luc constructs. (J) H&E and Safranin O/Fast Green staining of paraffin sections of scaffolds before implantation and after implantation, followed by immunohistochemistry for collagen I, IIa1, and X. n = 5 to 6 per group, two-way ANOVA with Geisser-Greenhouse corrections: different letters indicate P < 0.001 by Tukey’s post hoc test. (B) n = 3 to 8, one-way ANOVA; (F) n = 3 to 5 per group, two-way repeated measures ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test; (C, G, and I) two-way ANOVA: adjusted P values are shown above each time point for Sidak’s post hoc test.