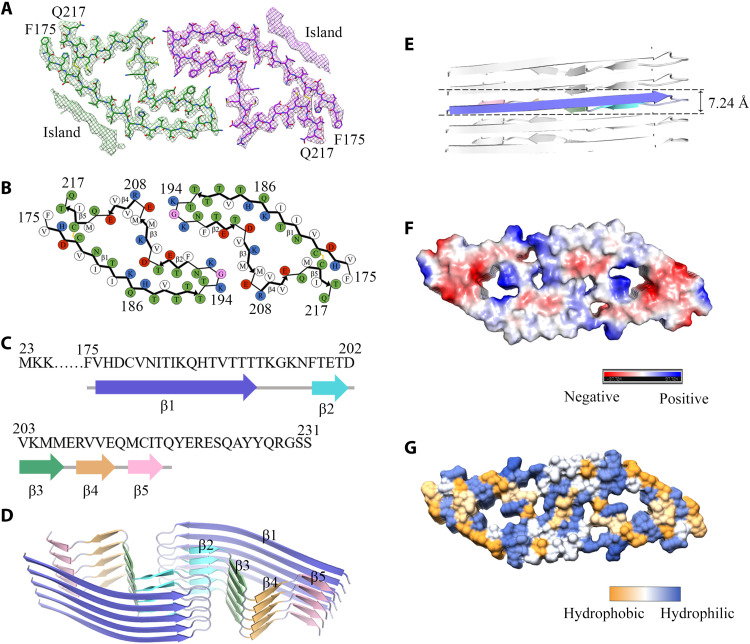
Fig. 3. Atomic structure of E196K fibrils.
(A) Cryo-EM map of E196K fibrils with the atomic model overlaid. Two identical densities (termed two islands) flanking the two protofibrils, which are colored green and purple, respectively. Each island is located on the opposing side of hydrophobic side chains of Val180, Ile182, and Ile184 in each monomer. (B) Schematic view of the E196K fibril core. Residues are colored as follows: white, hydrophobic; green, polar; red and blue, negatively and positively charged, respectively; and magenta, glycine. β strands are indicated with bold lines. E196K fibrils are stabilized by a disulfide bond (yellow line) formed between Cys179 and Cys214 in each monomer, also visible in (A). (C) Sequence of the fibril core comprising residues 175 to 217 from E196K, with the observed five β strands colored blue (β1), cyan (β2), green (β3), orange (β4), and pink (β5). The dotted line corresponds to residues 23 to 174 not modeled in the cryo-EM density. (D) Ribbon representation of the structure of an E196K fibril core containing five molecular layers and a dimer. (E) As in (D), but viewed perpendicular to the helical axis, revealing that the height of one layer of the subunit along the helical axis is 7.24 Å. (F) Electrostatic surface representation of the structure of an E196K fibril core containing five molecular layers and a dimer. (G) Hydrophobic surface representation of the structure of an E196K fibril core as in (D). (F and G) Two pairs of amino acids (Lys194 and Glu207; Lys196 and Glu200) from opposing subunits form four salt bridges at the zigzag interface of the two protofibrils. The surface of two opposing subunits is shown according to the electrostatic properties (F) or the hydrophobicity (G) of the residues.