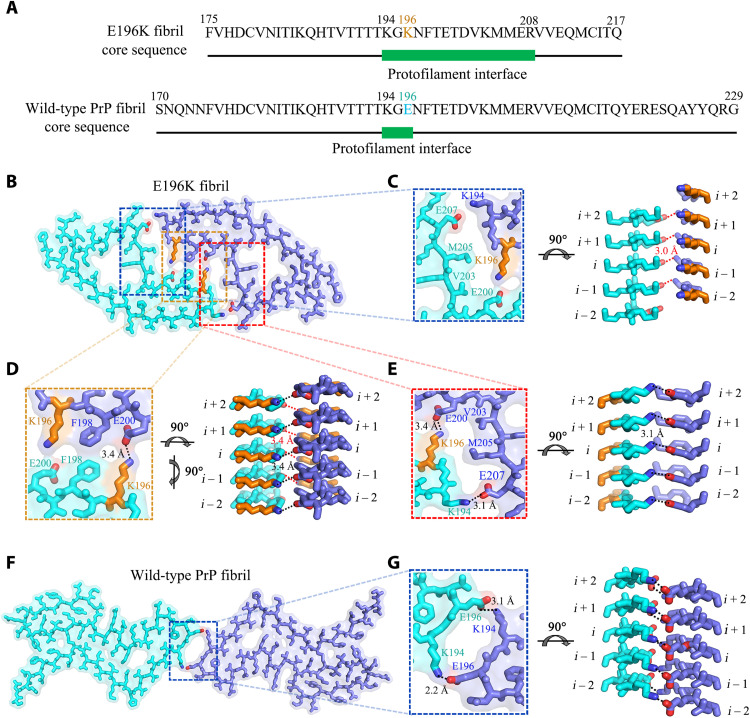
Fig. 4. Comparison of protofilament interfaces of E196K and wild-type fibrils.
(A) The primary sequences of the E196K fibril core and the wild-type fibril core. The green bar marks the region of the protofilament interface. Lys196 in E196K variant and Glu196 in wild-type PrP are highlighted in orange and cyan, respectively. (B and F) Two space-filled models overlaid onto stick representations of the E196K fibril (B) and the wild-type PrP fibril (PDB 6LNI) (33) (F), respectively, in which one protofibril is shown in cyan and another in blue. Lys/Glu pairs that form salt bridges are highlighted in red (oxygen atoms in Glu), blue (nitrogen atom in Lys), and orange (Lys196), and the dimer interface is magnified in (C) to (E) and (G). (C to E) Magnified top views of the three regions of the zigzag interface between E196K protofibrils, where four pairs of amino acids (Glu207 and Lys194; Glu200 and Lys196; Lys196 and Glu200; and Lys194 and Glu207) from opposing subunits form four salt bridges. Two side views (right) highlighting a strong salt bridge between Glu207 (i) and Lys194 or between Glu200 (i) and Lys196 from its opposing adjacent subunit (i − 1), with a distance of 3.0 or 3.4 Å (red). Two side views (right) highlighting a strong salt bridge between Lys196 (i) and Glu200 or between Lys194 (i) and Glu207 from its opposing subunit (i), with a distance of 3.4 or 3.1 Å (black). (G) A magnified top view of the dimer interface between wild-type PrP protofibrils, where two pairs of amino acids (Lys194 and Glu196; Glu196 and Lys194) from opposing subunits form two salt bridges. A side view (right) highlighting a strong salt bridge between Lys194 (i) and Glu196 or between Glu196 (i) and Lys194 from its opposing subunit (i), with a distance of 2.2 or 3.1 Å (black).