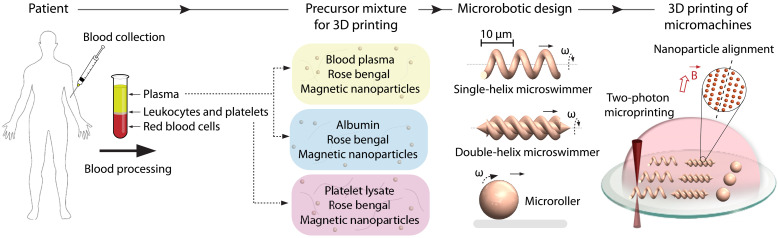
Fig. 1. A facile strategy for the 3D printed personalized micromachines from patient blood–derivable biomaterials.
Harvested blood from the patient can be rapidly and robustly processed to obtain blood plasma, albumin, and platelet lysate. We use these biomacromolecules to prepare the microfabrication precursor mixtures containing the photosensitizer rose bengal and magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for wireless powering and control. CADs of the micromachines are then realized by two-photon polymerization-based 3D printing. During the 3D printing process, we apply a uniform magnetic field in the direction perpendicular to the rotation axis of the micromachines to maximize the net magnetization by self-assembling the magnetic nanoparticles into directional chains.