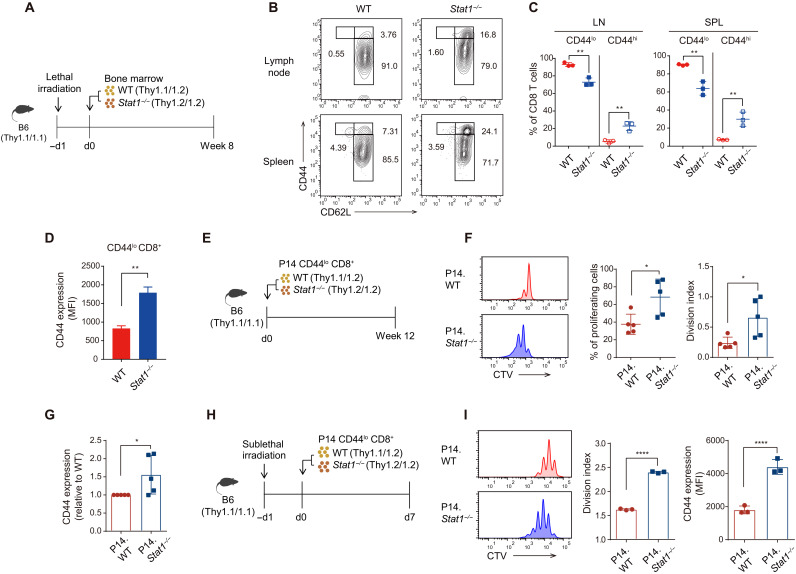
Fig. 2. Stat1−/− naïve CD8+ T cells show enhanced proliferation in a cell-intrinsic manner.
(A) Experimental scheme of generating BM chimera for (B) to (D). (B) Flow cytometry for CD44 and CD62L expression in CD8+ T cells derived from WT and Stat1−/− BM. (C) Percentage of CD44lo and CD44hi CD8+ T cells derived from WT and Stat1−/− BM. (D) CD44 expression levels in WT and Stat1−/− BM-derived CD44lo CD8+ T cells. MFI, mean fluorescence intensity. (E) Experimental scheme of adoptive transfer into B6 recipients for (F) and (G). (F) In vivo proliferation of WT and Stat1−/− P14 donor cells at 12 weeks after transfer. (G) Levels of CD44 expression in WT and Stat1−/− P14 donor cells of pre- and post-transfer. (H) Experimental scheme of adoptive transfer into irradiated (500 cGy) B6 recipients for (I). (I) In vivo proliferation and CD44 level of WT and Stat1−/− P14 donor cells at 7 days after transfer. The results are presented as means ± SEM. Data are representative of three to four independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ****P < 0.0001.