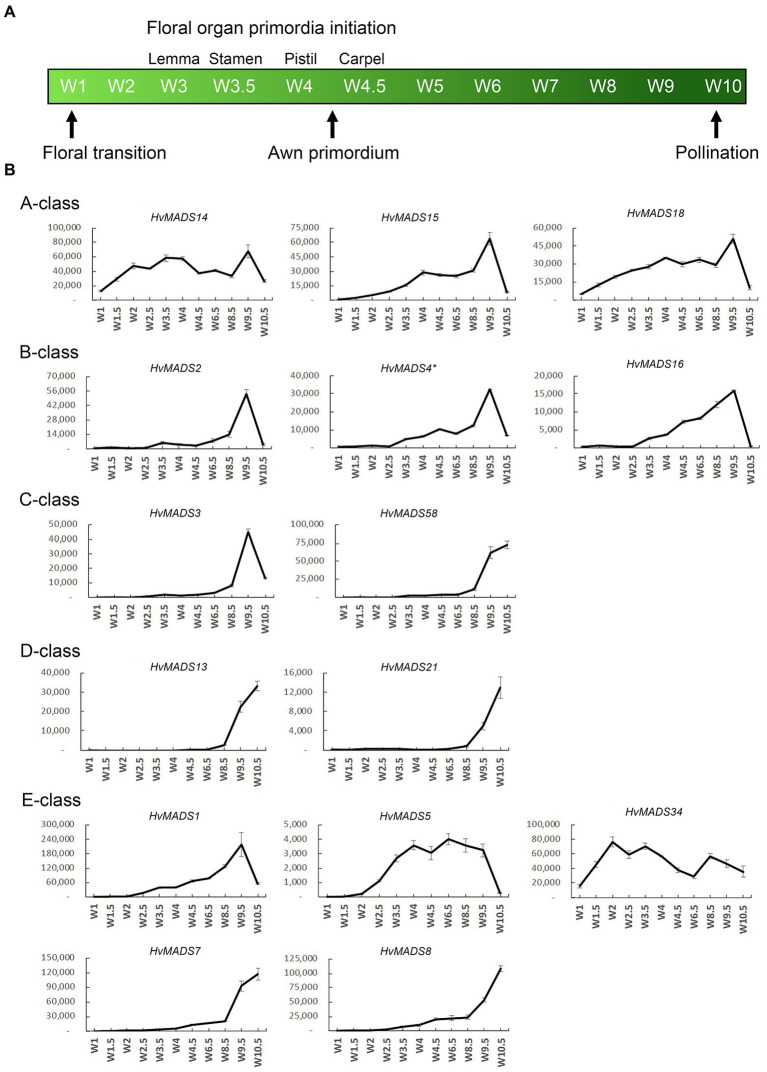
Figure 3.
(A) Waddington stages for barley and their relation to major developmental steps. (B) Transcript profiles of AP1, AP3/PI, AG(C), AG(D) and SEP MIKCc MADS-box genes in the shoot apex through inflorescence development as measured by the Waddington stage in Golden Promise. Error bars represent one standard deviation, based on technical replicates. A-class: The predicted A-class function in the outer floral organs predicts that transcript starts after W3, where the lemma primordium is first formed. However, expression of all three AP1 genes increases earlier, at the floral transition W1. AP3/PI: The expression of predicted B-class genes starts to increase at W3.5, where the stamen primordia are formed, and peaks right before pollination. AG(C): HvMADS3 and HvMADS58 both start expression around W3.5 when the stamen primordia appear, however HvMADS3 peaks before pollination and declines quickly afterwards, while HvMADS58 maintains peak expression through to W10. AG(D): HvMADS13 and HvMADS21 both start significant expression only after W6.5, well after the pistil primordium is formed, which first appears at W4. Their peak expression is after pollination. E-class: There is a clear difference between the LOFSEP genes HvMADS1, HvMADS5 and HvMADS34 that express earlier and sharply drop at pollination (W10) and HvMADS7 and HvMADS8 expression, which starts later around W3.5 and continues to rise through pollination.