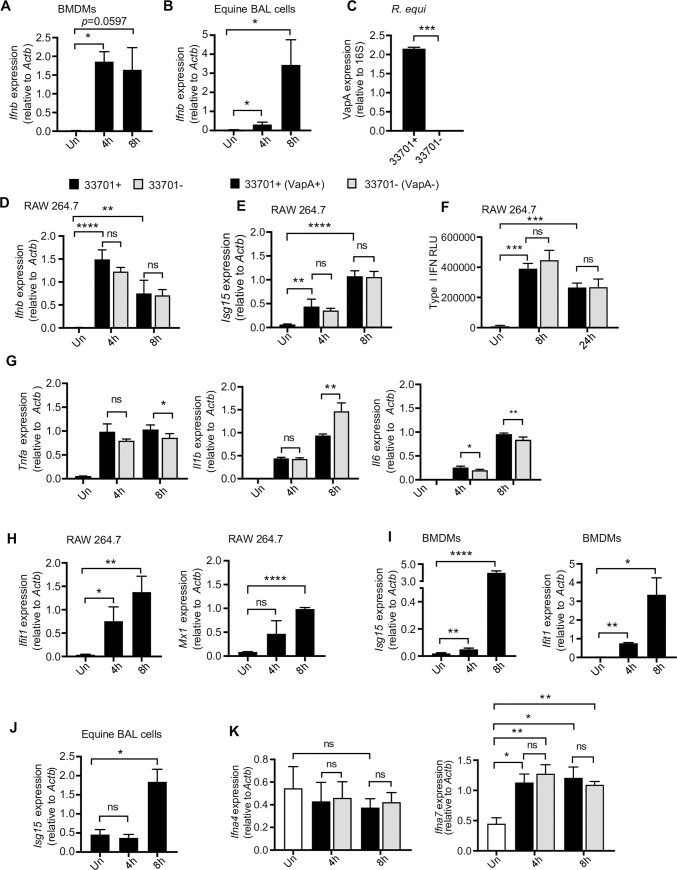
Fig 3. R. equi induces type I IFN expression during macrophage infection.
(A) RT-qPCR of Ifnb in R. equi-infected murine BMDMs. (B) As in (A) but in equine bronchoalveolar lavage cells. (C) RT-qPCR of VapA in R. equi 33701+ and 33701-. (D) RT-qPCR of Ifnb in RAW 264.7 cells infected with R. equi with (33701+) or without (33701-) VapA. (E) As in (D) but of Isg15. (F) ISRE reporter cell assay with relative light units (RLU) measured as a readout for secreted type I IFN protein in R. equi-infected macrophages. (G) As in (D) but Tnfa, Il1b, and Il6. (H) RT-qPCR of Ifit1 and Mx1 in RAW 264.7 cells infected with R. equi 33701+. (I) As in (A) but Isg15 and Ifit1. (J) As in (B) but Isg15. (K) As in (D) but Ifna4 and Ifna7. All RT-qPCRs are representative of at least 2 independent experiments and are the mean of 3 replicates ± SD, n = 3. Statistical significance was determined using Students’ t-test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, ns = not significant.