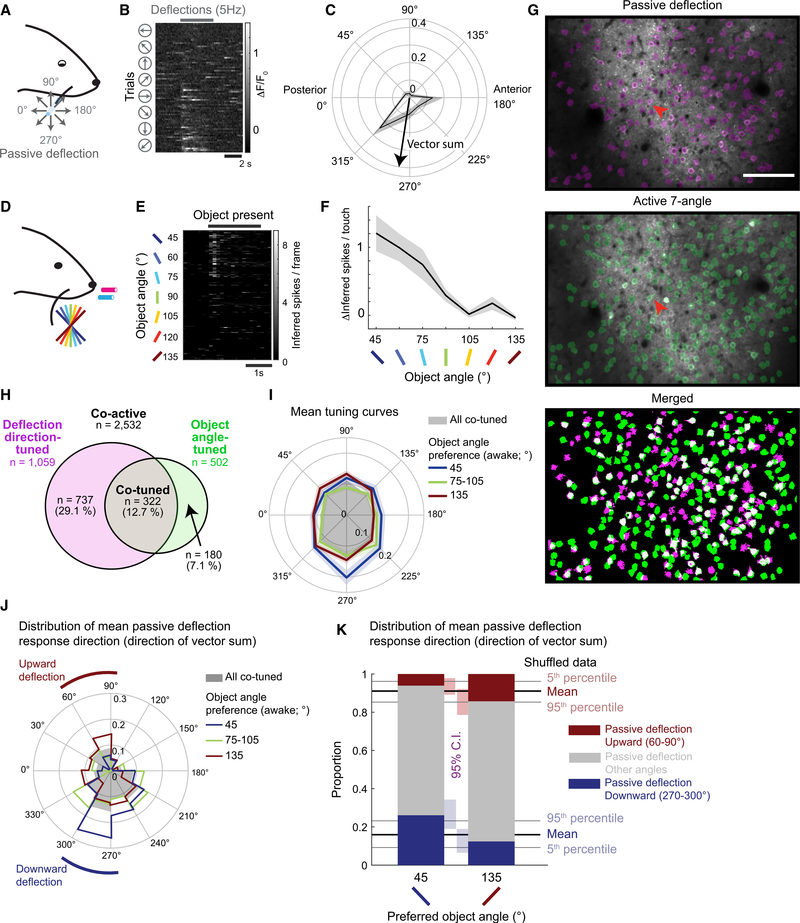
Figure 5. Weak Relationship between Passive Whisker Deflection-Direction and Object-Angle Tuning.
(A) C2 whisker piezo deflection with glass capillary under light isoflurane anesthesia.
(B) Example neuron response to passive whisker deflection (red arrow in G), sorted by deflection direction.
(C) Passive deflection-direction tuning curve from (B). Means ± SEMs of ΔF/F0.
(D) Active touch naive 7-angle test sessions.
(E) Neuronal response during active object touch, sorted by object angle. Same neuron as in (B).
(F) Object-angle tuning curve (means ± SEMs) from (E).
(G) Example FOV and overlaid ROI maps from matched anesthetized (top) and awake (center) experiments. The white neurons (bottom) are active in both sessions.
(H) Assortment of passive deflection-direction-tuned (magenta), active object-angle-tuned (green), and tuned in both sessions (co-tuned; gray), among all matched co-active neurons (white in G).
(I) Mean deflection-direction tuning curves of all co-tuned neurons (gray), overlaid with those preferring 45° (red), 75°–105° (green), or 135° (blue) object angle during naive 7-angle test sessions. Lighter colors are SEMs.
(J) Distribution of mean passive deflection response direction of all co-tuned neurons (gray), or preferring 45° (red), 75°–105° (green), or 135° (blue) object angle during naive 7-angle test sessions.
(K) Proportion of mean passive deflection response direction within neurons that preferred 45° or 135° object during naive 7-angle test sessions. Passive directions grouped by upward (60°–90°; red), downward (270°–300°; blue), and other directions (gray).
See also Figure S5.