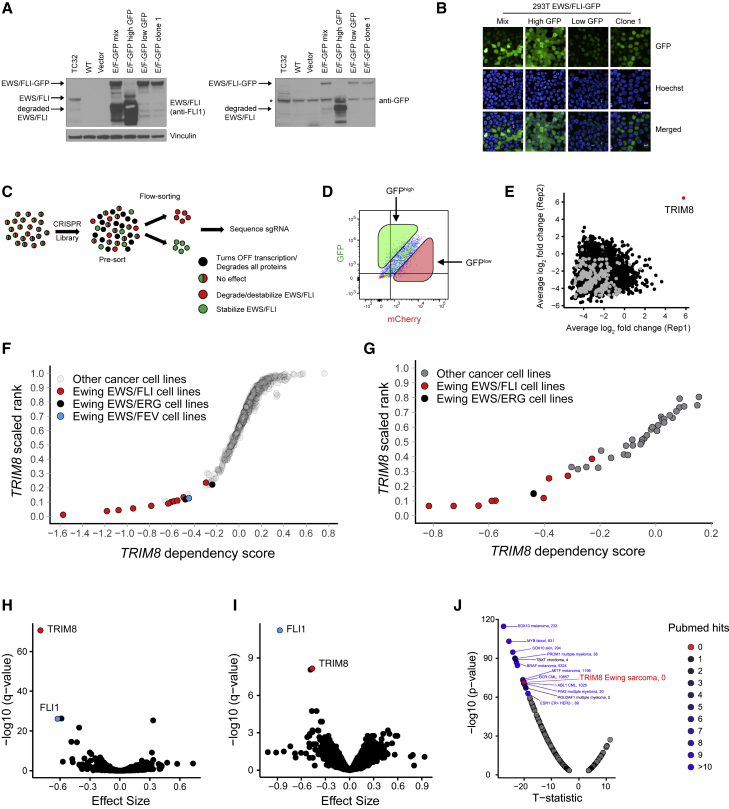
Figure 1.
CRISPR screens identify TRIM8 as a regulator of EWS/FLI protein stability and a selective dependency in Ewing sarcoma
(A and B) Immunoblot and images showing the expression level and localization of EWS/FLI-GFP in the reporter cell line and subpopulations. ∗Indicates a non-specific band.
(C and D) Schematic of flow cytometry-based CRISPR screening pipeline and the gating strategy used in the screen.
(E) Scatterplot showing average log2 fold changes in sgRNA abundance in replicates in the GFPhigh-sorted population. Negative control guides are highlighted in gray. sgRNAs targeting TRIM8 are highlighted in red. Each dot represents an average of log2 fold changes for four independent sgRNAs per gene.
(F and G) Scatterplots showing Ewing sarcoma relative dependency on TRIM8 in screens with the Avana (F) and GecKO (G) libraries. The x axis shows the gene’s dependency score in each cell line. The y axis shows the gene’s dependency rank in an individual cell line.
(H and I) Comparison of 14 Ewing sarcoma with 724 other cancer cell lines (H) and 11 Ewing sarcoma with 32 other cancer cell lines (I) demonstrates enrichment of TRIM8 dependency in Ewing sarcoma. Each circle represents a single gene. The x axis shows the effect size, which is the mean difference of dependency scores in Ewing sarcoma cell lines compared with other lines screened. Negative effect size indicates that Ewing sarcoma cells are more dependent on that gene compared with other cancer cell lines screened. The y axis shows the significance calculated as –log10(q value) from empirical-Bayes-moderated t statistics with Benjamini-Hochberg correction.
(J) A scatterplot showing ranked disease-enriched dependency in the Avana library (n = 738). The x axis shows the t statistics and the y axis shows the significance calculated as –log10(q value) from empirical Bayes-moderated t statistics with Benjamini-Hochberg correction. PubMed hits represent the number of papers retrieved when searched on PubMed.