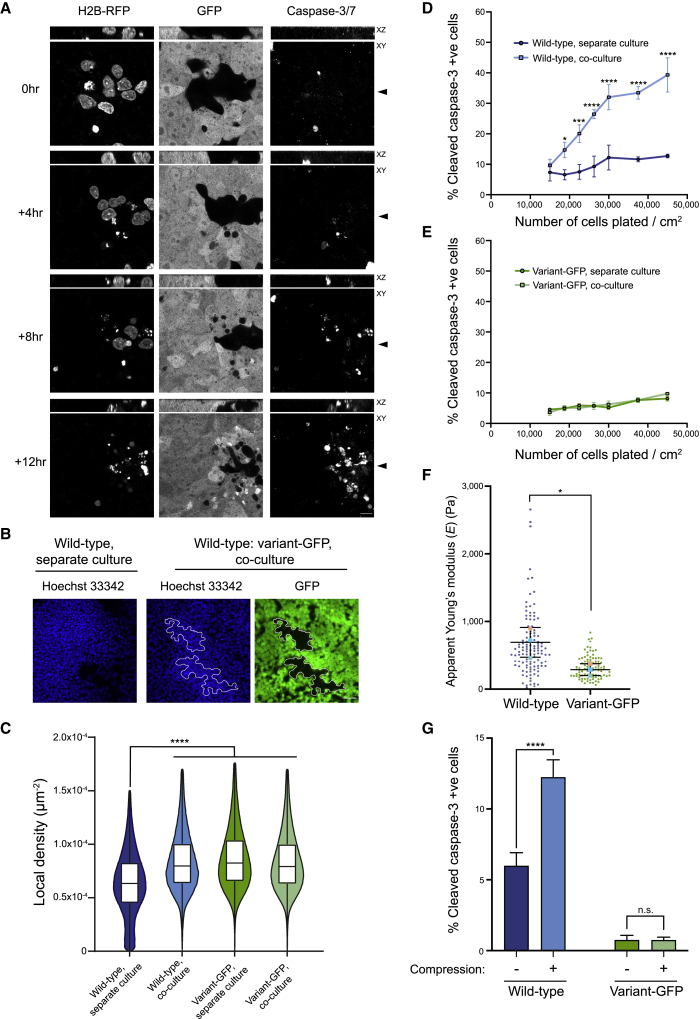
Figure 3.
Wild-type cells are corralled by variants into areas of high cell density
(A) Time-lapse images of wild-type-RFP and variant-GFP cells in co-culture from day 2 in the presence of live caspase-3/7. Closed arrowheads denote the position of the z axis within the x-y plane. Scale bar: 10 μm.
(B) Corralling of wild-type cells by variant-GFP counterparts. The outlined areas in the middle and right panels indicate regions of co-culture harboring wild-type cells. Scale bar: 50 μm.
(C) Cell density of wild-type and variant-GFP cells grown either separately or in co-cultures.
(D and E) Percentage of wild-type (D) and variant-GFP (E) cells positive for cleaved caspase-3 grown either in separate culture or upon co-culture at increasing plating densities.
(F) Apparent Young’s modulus (E) of wild-type and variant-GFP cells. Small points indicate individual cells and larger circles indicate a mean from each of the three independent experiments.
(G) Cell-compaction assay; percentage of wild-type and variant-GFP cells positive for cleaved caspase-3 indicator of apoptosis on uncompressed or compressed membranes (denoted as - and + compression, respectively). Data are the mean of three independent experiments ± SD. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA.
Data represent the values of individual cells (C) or the mean (D–G) from three independent experiments (C–G) ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA (C and G); two-way ANOVA, followed by Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparisons test (D and E) or Student’s t test (F); n.s., nonsignificant; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.