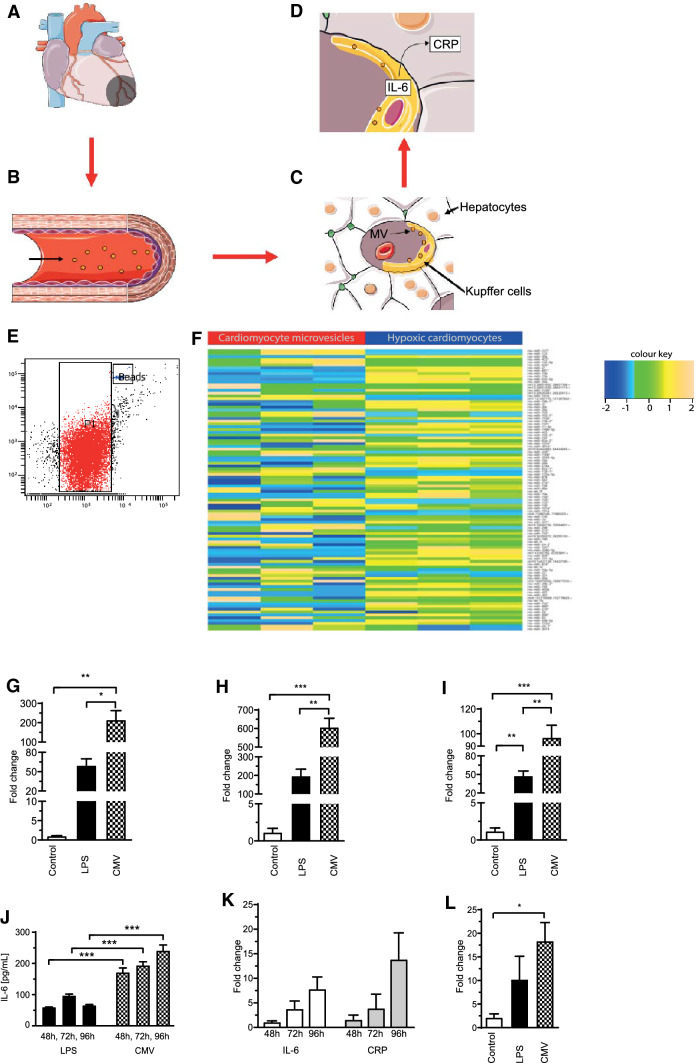
Fig. 1.
Suggested model of CMV-mediated CRP expression in hepatocytes. For more information see text, underlying images of Fig. 1a–d were adapted from http://smart.servier.com/ under a creative commons licence (a–d). Microvesicles were successfully isolated from the supernatant of hypoxic H9c2 cardiomyocytes. P1 indicates the microvesicle gate, “beads” indicates a gate for standardized counting beads (e). Next-generation sequencing revealed that CMV contain a distinct pattern of miRNA compared to their parent cells as shown by the heat map. The color key indicates the z-score of the normalised read-count of individual miRNAs. Most miRNAs had higher read counts in hypoxic cells than in CMV (f). IL-6 expression was upregulated as shown by qPCR using RNA from THP-1 macrophages after incubation with H9c2 CMV for 48 (g), 72 (h) or 96 h (i). Induction of IL-6 expression by CMV in THP-1 macrophages was verified on a protein level by ELISA after 48, 72 and 96 h. IL-6 levels were increased after incubation with CMV even compared to the positive control (LPS) (j). CMV induced a gradual rise in IL-6 and CRP expression in the co-culture of HepG2 and THP-1 cells as determined by qPCR (k). CRP increase was also higher compared to the negative control exemplified after 96 h (l)