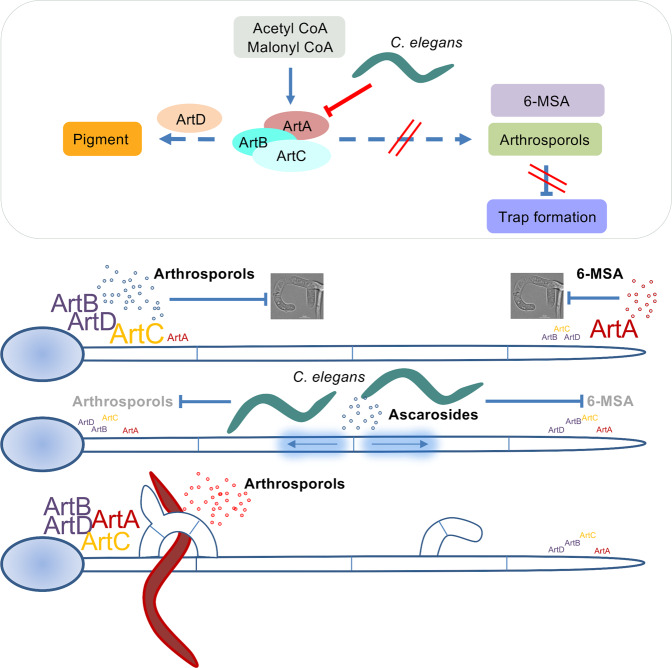
Fig. 6. Scheme of the action of the artA-gene cluster and the effect of the presence of C. elegans.
Gradients of 6-MSA, arthrosporols, and ascarosides control trap formation in D. flagrans. 6-MSA is produced at hyphal tips, while further back 6-MSA is converted to arthrosporols. Both compounds block trap formation. After successful attraction of a large number of nematodes by 6-MSA and other molecules, the concentration of ascarosides raises above a threshold. This will result in the downregulation of the artA-gene cluster genes, which in turn causes a decrease of 6-MSA and arthrosporols. If their concentration falls below a threshold, repression of trap formation is released, and traps are formed to catch the worms. After the digestion of trapped worms (red color), artA-gene cluster gene expression resumes, and increasing arthrosporols concentrations prevent unnecessary and excessive trap formation. Bigger font size symbolizes higher expression levels.