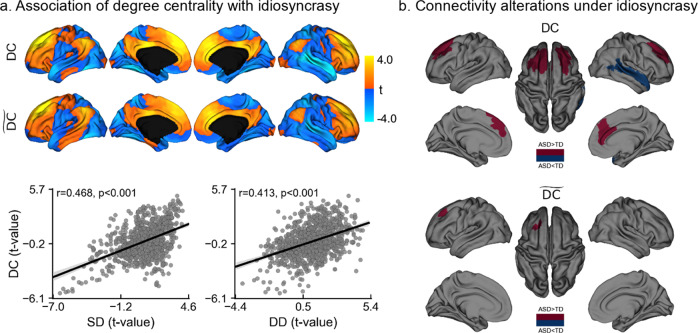
Fig. 5. Association of degree centrality with idiosyncrasy.
a Statistical t-maps (top) of areas showing differences in degree centrality between ASD and TD before (i.e., DC) and after controlling for idiosyncrasy (i.e., ), and Pearson’s correlation (bottom) of DC t-map with t-maps of surface (SD) and diffusion (DD) distances. b Regions showing significant DC increases (red) and decreases (blue) in ASD before (top) and after (bottom) controlling for idiosyncrasy. Idiosyncrasy is represented with SD and DD as additional covariates. Shaded areas around the regression lines denote a 95% confidence interval.