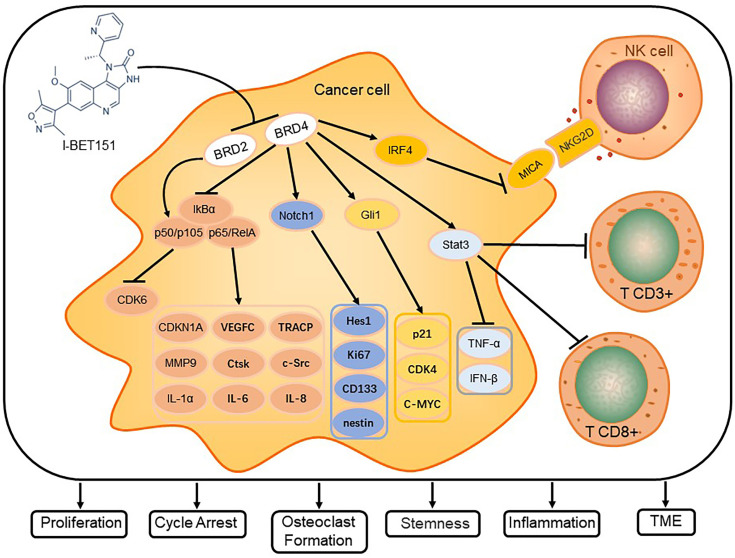
Figure 2.
I-BET151 affects the signal transduction in cancer cells and modulates critical cellular processes. I-BET151 specifically inhibits BRD2 and BRD4, decreases the intracellular content of p50/p105, diminishes the degradation of IkB-α, prevents the dissociation of p50/p105 and p65/RelA from IkB-α and their transport into the nucleus, and decreases the activity of NF-B signal transduction. In addition, I-BET151 reduces the binding of BRD4 to the Notch1 and Gli1 promoter regions, inhibits the transcription of Notch1 and Gli1, and causes the target molecules of Notch and Hh signaling pathways to change. In the aspect of influencing tumor microenvironment, I-BET151 not only targets BRD4, which leads to the increase of MICA expression and promoting NK cell degranulation, but also inhibits Stat3 signal, which leads to more CD3+ and CD8+ cells in tumors. Eventually, I-BET151 leads to cell cycle arrest, inhibition of cancer cell proliferation, stemness of stem cells, inflammatory factor release, osteoclast formation and regulation of TME.