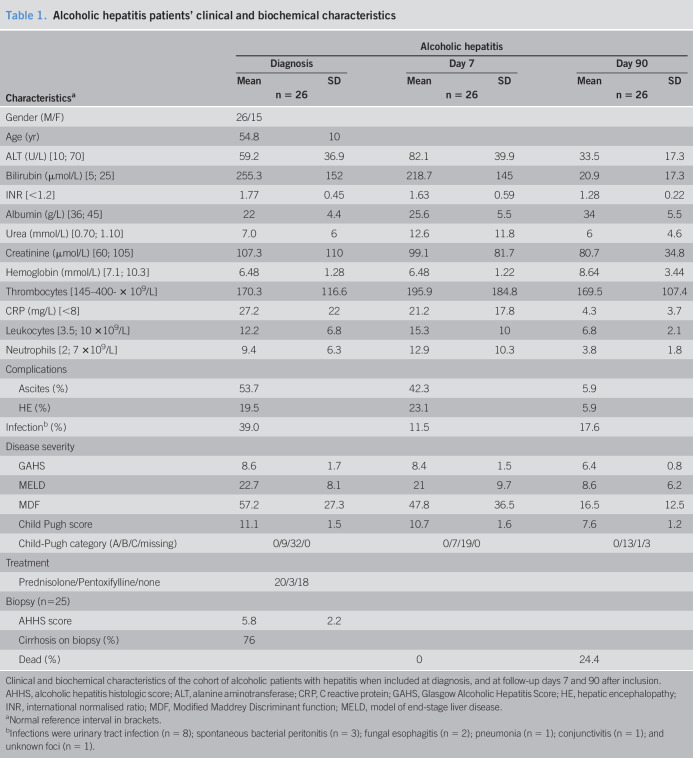
Table 1.
Alcoholic hepatitis patients' clinical and biochemical characteristics
| Characteristicsa | Alcoholic hepatitis | |||||
| Diagnosis | Day 7 | Day 90 | ||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| n = 26 | n = 26 | n = 26 | ||||
| Gender (M/F) | 26/15 | |||||
| Age (yr) | 54.8 | 10 | ||||
| ALT (U/L) [10; 70] | 59.2 | 36.9 | 82.1 | 39.9 | 33.5 | 17.3 |
| Bilirubin (μmol/L) [5; 25] | 255.3 | 152 | 218.7 | 145 | 20.9 | 17.3 |
| INR [<1.2] | 1.77 | 0.45 | 1.63 | 0.59 | 1.28 | 0.22 |
| Albumin (g/L) [36; 45] | 22 | 4.4 | 25.6 | 5.5 | 34 | 5.5 |
| Urea (mmol/L) [0.70; 1.10] | 7.0 | 6 | 12.6 | 11.8 | 6 | 4.6 |
| Creatinine (μmol/L) [60; 105] | 107.3 | 110 | 99.1 | 81.7 | 80.7 | 34.8 |
| Hemoglobin (mmol/L) [7.1; 10.3] | 6.48 | 1.28 | 6.48 | 1.22 | 8.64 | 3.44 |
| Thrombocytes [145–400- × 109/L] | 170.3 | 116.6 | 195.9 | 184.8 | 169.5 | 107.4 |
| CRP (mg/L) [<8] | 27.2 | 22 | 21.2 | 17.8 | 4.3 | 3.7 |
| Leukocytes [3.5; 10 ×109/L] | 12.2 | 6.8 | 15.3 | 10 | 6.8 | 2.1 |
| Neutrophils [2; 7 ×109/L] | 9.4 | 6.3 | 12.9 | 10.3 | 3.8 | 1.8 |
| Complications | ||||||
| Ascites (%) | 53.7 | 42.3 | 5.9 | |||
| HE (%) | 19.5 | 23.1 | 5.9 | |||
| Infectionb (%) | 39.0 | 11.5 | 17.6 | |||
| Disease severity | ||||||
| GAHS | 8.6 | 1.7 | 8.4 | 1.5 | 6.4 | 0.8 |
| MELD | 22.7 | 8.1 | 21 | 9.7 | 8.6 | 6.2 |
| MDF | 57.2 | 27.3 | 47.8 | 36.5 | 16.5 | 12.5 |
| Child Pugh score | 11.1 | 1.5 | 10.7 | 1.6 | 7.6 | 1.2 |
| Child-Pugh category (A/B/C/missing) | 0/9/32/0 | 0/7/19/0 | 0/13/1/3 | |||
| Treatment | ||||||
| Prednisolone/Pentoxifylline/none | 20/3/18 | |||||
| Biopsy (n=25) | ||||||
| AHHS score | 5.8 | 2.2 | ||||
| Cirrhosis on biopsy (%) | 76 | |||||
| Dead (%) | 0 | 24.4 | ||||
Clinical and biochemical characteristics of the cohort of alcoholic patients with hepatitis when included at diagnosis, and at follow-up days 7 and 90 after inclusion.
AHHS, alcoholic hepatitis histologic score; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; CRP, C reactive protein; GAHS, Glasgow Alcoholic Hepatitis Score; HE, hepatic encephalopathy; INR, international normalised ratio; MDF, Modified Maddrey Discriminant function; MELD, model of end-stage liver disease.
Normal reference interval in brackets.
Infections were urinary tract infection (n = 8); spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (n = 3); fungal esophagitis (n = 2); pneumonia (n = 1); conjunctivitis (n = 1); and unknown foci (n = 1).