Figure 3. Isolate Relatedness, Investigation Association, and Antibiotic Resistance Patterns of Isolates From Human Patients and Dogs Linked to Pet Stores, US, 2011–2020.
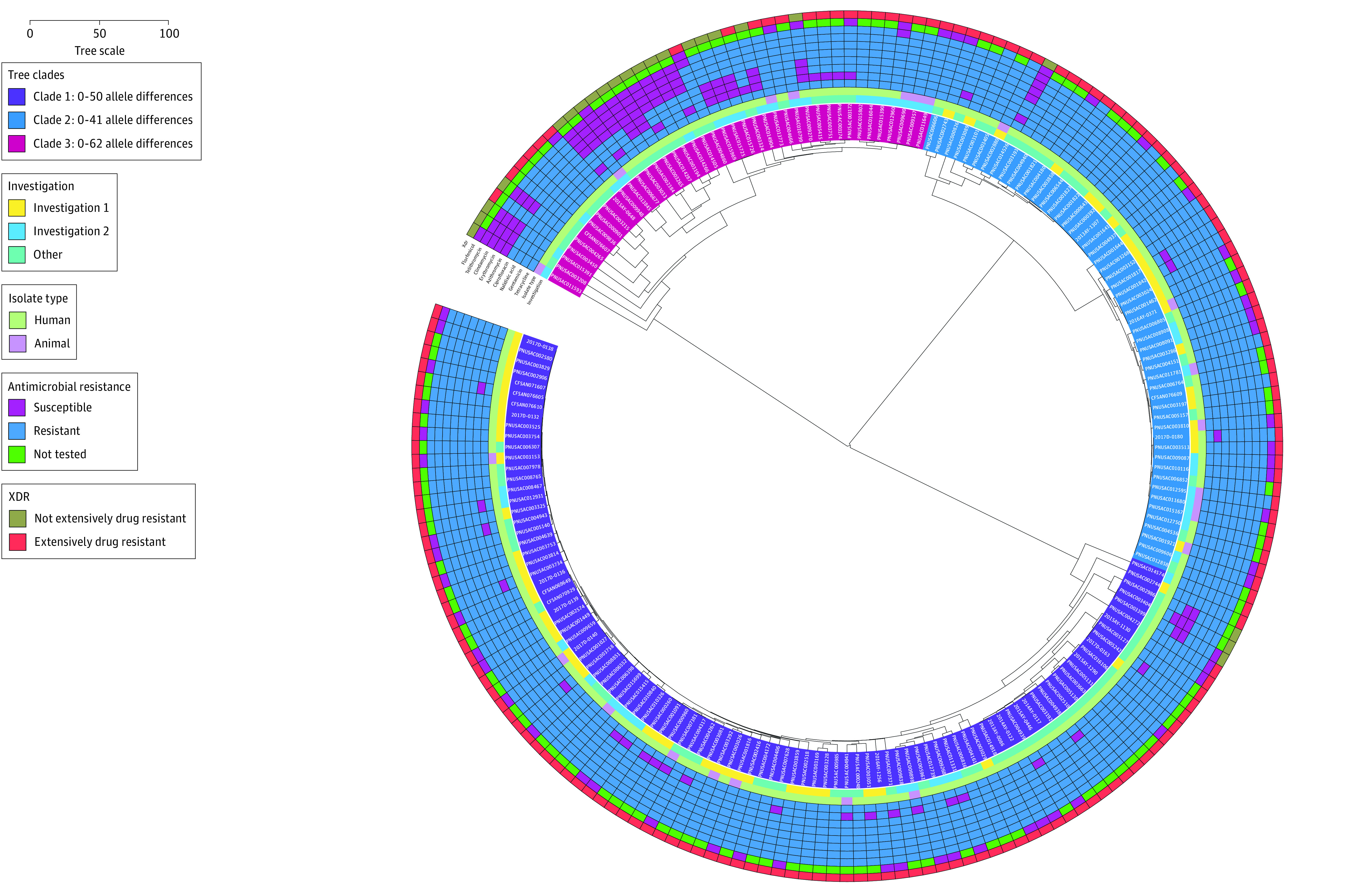
Isolate relatedness was assessed using core genome multilocus sequence typing; the figure was generated using Interactive Tree of Life software, version 5 (BioByte Solutions).18 Antibiotic resistance determination was based on antibiotic susceptibility testing results when available (n = 72) and otherwise on the presence of known resistance determinants in the bacterial genome for all agents except florfenicol. Isolate identifications are shaded according to the clade to which they belong. Other shaded rings correspond to the investigation type (innermost ring); isolate type; susceptibility status for tetracycline, gentamicin, nalidixic acid, ciprofloxacin, azithromycin, erythromycin, clindamycin, telithromycin, and florfenicol; and extensively drug-resistant (XDR) status (outermost ring). The number of allele differences between isolates is proportionate to the combined distance to the nearest common node; the distance corresponding to 100 allele differences is shown. An interactive version of this figure is available at https://itol.embl.de/shared/2DT03vJtQjoQN.
