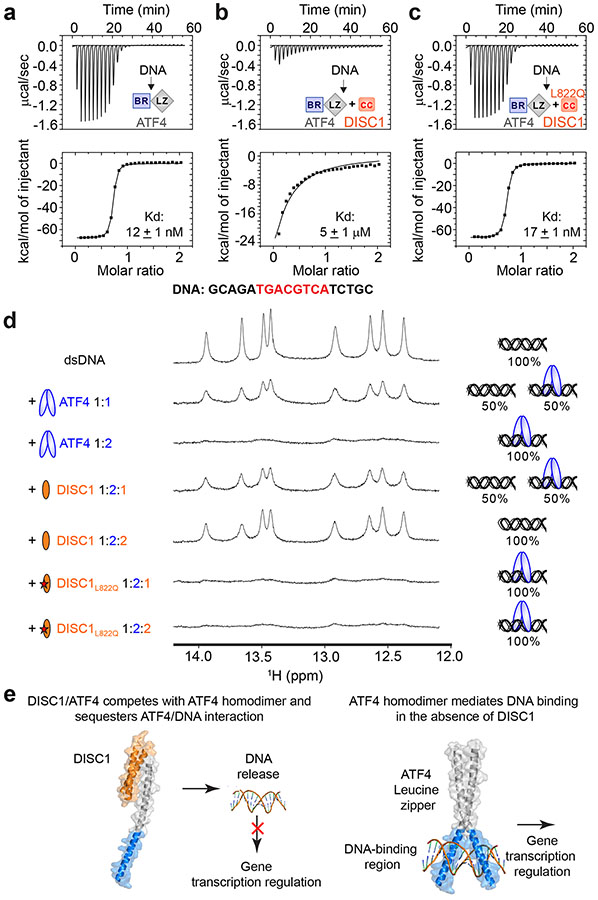
Figure 4.
DISC1 prevents ATF4 from binding to DNA. (a-c) ITC-based measurements showing an ATF4 homodimer bound to double strand DNA (dsDNA: GCAGATGACGTCATCTGC) with a very strong affinity (a). Addition of equal molar amount of DISC1-CC (i.e. DISC1:ATF4 = 1:1) led to a ~500 fold reduction of the binding affinity between ATF4 and dsDNA (b), and the L822Q-DISC1-CC mutant did not affect the DNA binding ability of ATF4 (c). (d) 1D 1H NMR spectra showing the imino proton resonances from the ATF4 binding dsDNA. Annealed double stranded DNA (a) was titrated with 1:1 and 1:2 molar ratios of ATF4, showing that the imino proton peaks of DNA are selectively broadened upon ATF binding. When DISC1-CC was added into the DNA/ATF4 complex from 1:1:2 (DISC1WT: DNA: ATF4) to 2:1:2 molar ratio, the DNA was released from ATF4 as indicated by the recovery of its imino peaks. In contrast, addition of the L822Q-DISC1-CC mutant to the DNA/ATF4 complex from 1:1:2 (DISC1L822Q: DNA: ATF4) to 2:1:2 molar ratio did not release DNA from ATF4. We did not calibrate the peak intensities of the NMR signals during the titrations, so that the signals representing the DISC1/ATF4 binding-induced DNA release appeared weaker due to the sample dilution upon adding DISC1. (e) A mechanistic model depicting DISC1 binding-induced inhibition of the ATF4/DNA interaction and ATF4-mediated transcriptional regulation.