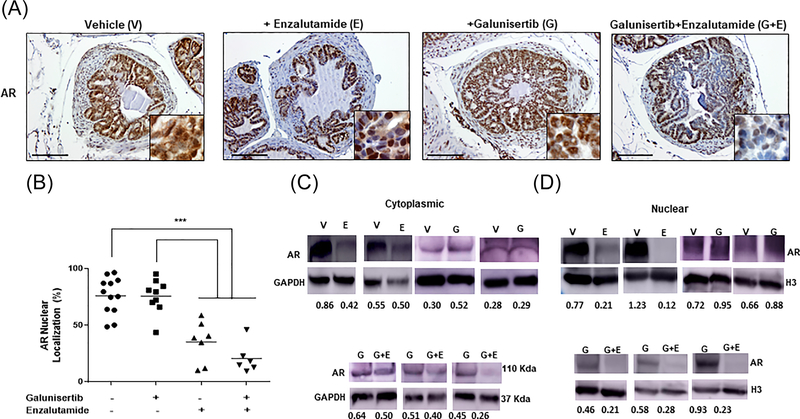
FIGURE 3.
Effect of TGF-β signaling blockade on nuclear AR expression. Panel A shows representative images for AR immunoreactivity in prostate tumors after the various treatments (Figure 1A). Treatment with enzalutamide as a single agent and in combination with galunisertib reulted in a marked reduction of nuclear AR levels (magnification ×100, insert ×400). Panel B reveals the numerical analysis of the immuoreactivity data indicating that in response to enzalutamide alone and the combination of galunisertib and enzalutamide there was a significant decrease of nuclear AR levels in prostate tumors. Galunisertib monotherapy had no significant effect on AR protein levels and nuclear localization compared to vehicle control mice (panels A and B). Panels C and D indicate representative Western blots profiling AR expression in cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions from prostate tumor lysates; treatment with the TβRI inhibitor alone had no marked effect on AR levels compared to controls, while the antiandrogen, enzalutamide alone reduced nuclear AR. The combination treatment of enzalutamide and galunisertib led to a marked decrease in nuclear AR compared to galunisertib monotherapy (panels C and D). Western blotting was performed as described in section 2.