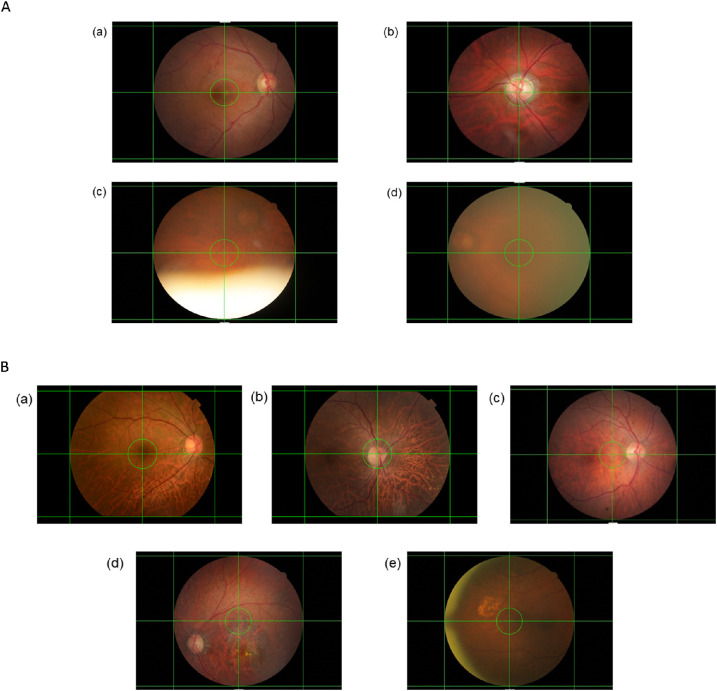
Figure 2.
(A) Examples of retinal photographs with different levels of image quality. A gradable retinal photograph had to fulfill both of the following criteria: (1) less than 25% of the peripheral area of the retina was unobservable due to artifacts, and (2) the center region of the retina had no significant artifacts. (a, b) Gradable and absence of any artifacts; (c) ungradable as more than 25% of the peripheral area of the retina was unobservable due to the presence of eyelid; (d) ungradable due to presence of significant artifact in the center region. (B) Example of retinal photographs with different fields of view. (a) Macula-centered; (b) optic-disc-centered; (c–e) off-centered. Horizontal and vertical auxiliary lines were added to locate the center region of the retinal photograph, which was bounded by a green circle. The center region of a retinal photograph is defined as the circular region of radius (in pixels) with the largest integer not greater than one-tenth the width of the image at the center of the image. A green circle bounded the center region of the retinal photograph.