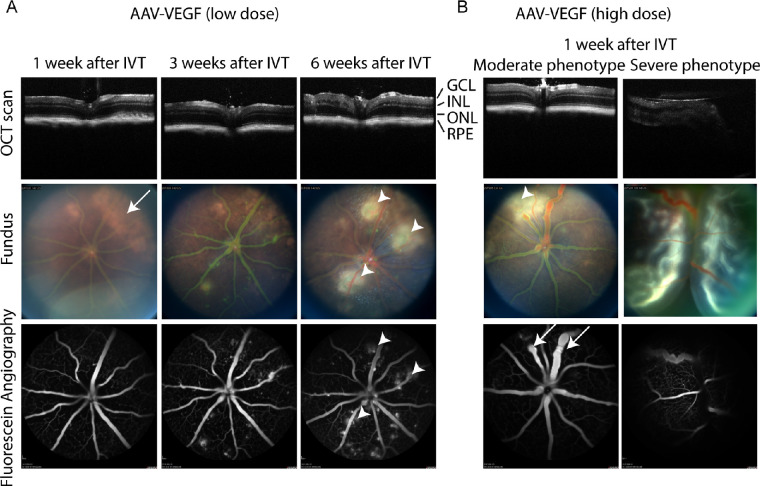
Figure 2.
AAV-VEGF injection led to vascular pathologies in mouse eyes. (A) IVT injection of low dose AAV-VEGF led to progressive increase of vascular permeability starting from 3 weeks after injection as seen by FFA in the same mouse eye. White spots co-localizing the leakage areas were found by fundus imaging (arrowheads). Bright, unspecific areas were observed at earlier timepoints (arrow) that fainted over time and were also seen in AAV-stuffer control eyes (see Supplementary Fig. S2). (B) IVT injection of high dose AAV-VEGF led to focally dilated or constricted vessels (arrow) and vascular leakage 1 week after injection in 50% of the mice (“moderate phenotype,” left column). There was 50% of the mice that developed severe pathologies, including retinal detachment (right column). GCL = ganglion cell layer; INL = inner nuclear layer; ONL = outer nuclear layer; RPE = retinal pigment epithelium; low dose = 1 × 108; high dose = 1 × 109 VG/eye.