Figure 3.
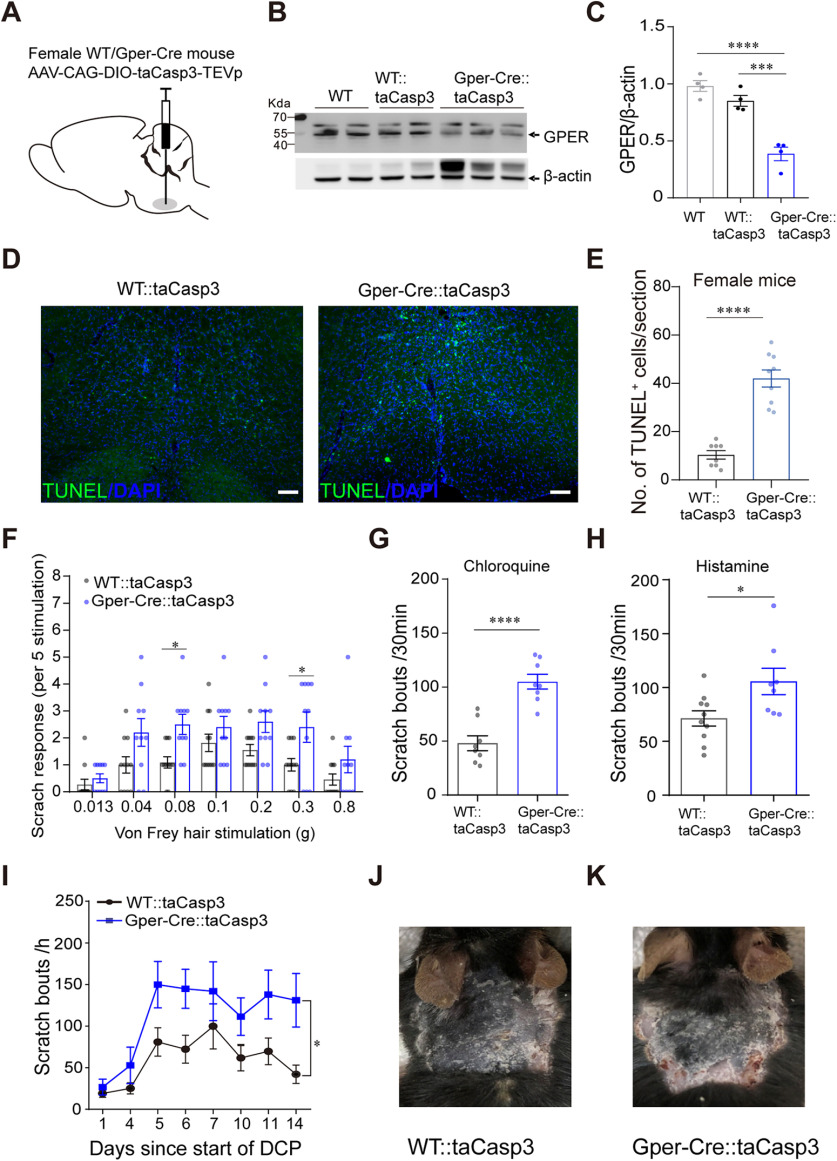
Selective ablation of RVM GPER+ neurons aggravates acute and chronic itch. A, Schematic showing the injection of AAV-DIO-taCasp3 into the RVM of female WT or Gper-Cre mice. B, C, Western blot showing the decreased expression of GPER protein in the RVM of Gper-Cre mice 35 d after AAV-DIO-taCasp3 injection; n = 4 mice for each group; one-way ANOVA and Tukey's post hoc test were used to assess statistical differences. F = 36.92, p = 0.0003 for WT::taCasp3 versus Gper-Cre::taCasp3, p < 0.0001 for WT versus Gper-Cre::taCasp3. D, Apoptotic neurons in the RVM were examined using TUNEL staining. Scale bar, 50 µm. E, The number of apoptotic neurons in the RVM of female WT or Gper-Cre mice injected with AAV-CAG-DIO-taCasp3-TEVp; n = 8–9 slides from three mice, unpaired Student's t test. p < 0.0001, t = 7.671, df = 15. F, Acute mechanical itch in GPER+ neuron-ablated Gper-Cre mice and control mice; n = 10–11 mice for each group; two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's post hoc test. F(1,133) = 26.65; 0.08 g, p = 0.0299; 0.3 g, p = 0.0316. G, H, Ablation of RVM GPER+ neurons increased the scratching behavior in response to chloroquine (150 µg/20 µL; G) and histamine (500 µg/20 µL; H); n = 8–10 mice for each group; unpaired Student's t test. p < 0.0001, t = 5.855, df = 14 (G); p = 0.0215, t = 2.548, df = 16 (H). I, Ablation of RVM GPER+ neurons increased the scratch bouts induced by DCP on every testing day; n = 7–9 mice for each group. Difference in area under curve (AUC) was compared by unpaired Student's t test. p = 0.0115, t = 2.908, df = 14. J, K, Representative photograph of neck skin in DCP-treated female WT (J) and Gper-Cre (K) mice injected with AAV-DIO-taCasp3.