Figure 1.
SypHy reveals vesicular fusion along reticulospinal axons
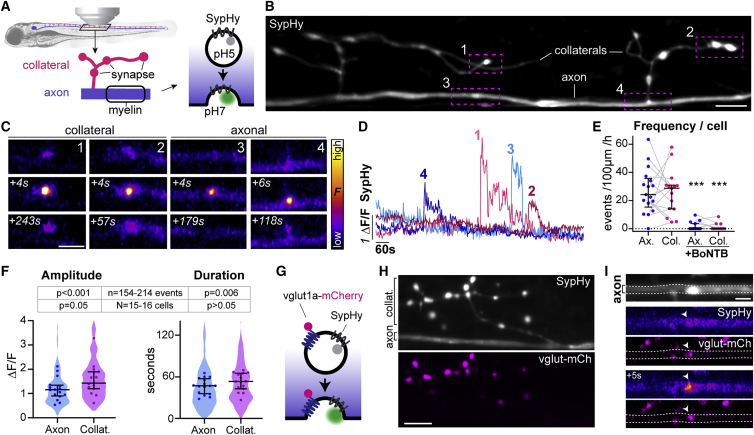
(A) Morphology of reticulospinal axons in the developing zebrafish spinal cord. SypHy, a synaptophysin-pHluorin fusion protein, reports synaptic vesicle exocytosis.
(B) Individual SypHy+ reticulospinal axon (dorsal up) with synapse-bearing collateral branches.
(C and D) SypHy events at collaterals and axon (C) and fluorescence time courses (D).
(E) SypHy frequency is similar in axons and collaterals (gray lines shows respective events of same cell); and abolished in BoNTB+ neurons (p = 0.82 Ax versus Col; p < 0.001 Ax versus Ax+BoNTB; p < 0.001 Col versus Col+BoNTB; Mann-Whitney test, 17 control axons from 16 animals; 15 BoNTB axons from 15 animals).
(F) Amplitude and duration of SypHy events in reticulospinal axons. Violin plots represent all analyzed events and circles denote average per axon (p = 0.054 Ax versus Col amplitude, p = 0.264 Ax versus Col duration, Mann-Whitney tests; n = 154 axonal and 214 collateral events from N = 16 axons from 15 animals).
(G–I) vglut1a-mCherry co-expression with SypHy (G) shows co-localization at synaptic terminals in collateral branches (H) and at axonal puncta (I).
Scale bars, 5 μm (B, H, and I), 2 μm (C). Graphs display median and interquartile range.