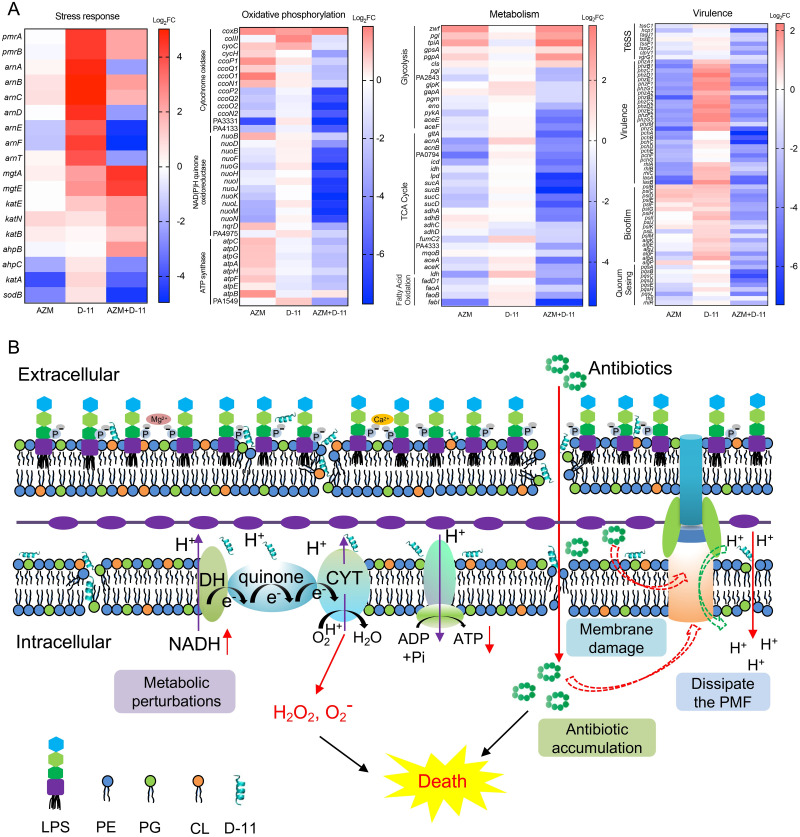
Fig 4. Transcriptome analysis and proposed synergy action model.
(A) The effect of D-11 alone, azithromycin alone or the combination over the expression of several genes involved in stress response, oxidative phosphorylation, metabolism and virulence. AZM, 8 μM azithromycin treatment alone; D-11, 4 μM D-11 treatment alone; AZM + D-11, the combination of azithromycin and D-11 treatment. (B) Proposed action mechanism for the synergy of D-11 in combination with antibiotics. D-11 restores the susceptibility of P. aeruginosa to antibiotics through membrane-mediated mechanisms by interacting with LPS, CL and PG. These reactions trigger membrane depolarization and induce membrane dysfunction, further resulting in metabolic perturbations and ROS accumulation. In addition, more antibiotics rapidly accumulate inside bacteria due to the increased membrane permeability and dysfunction of efflux pumps mediated by the dissipation of membrane potential. The accumulation of ROS and antibiotics working together resulted in the death of cells.