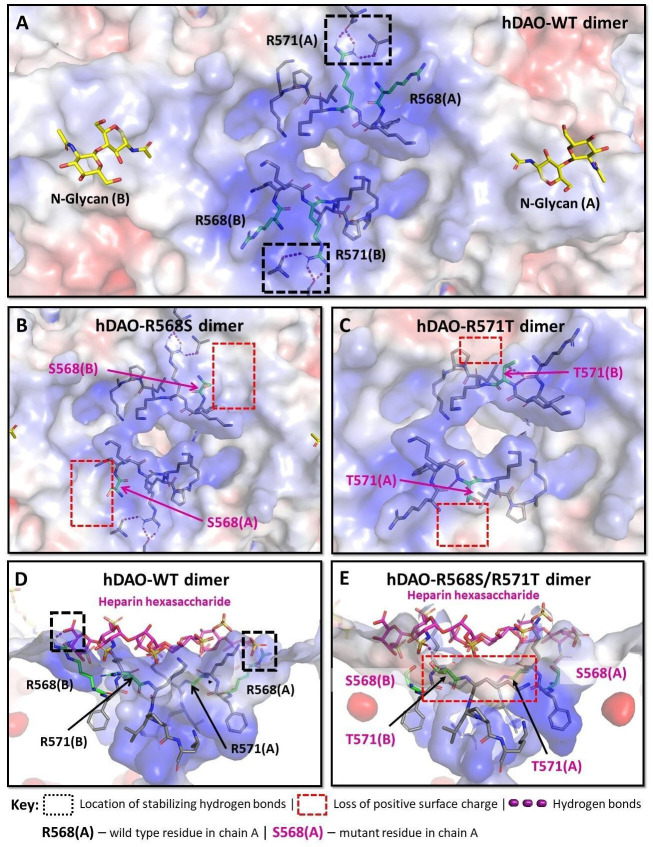
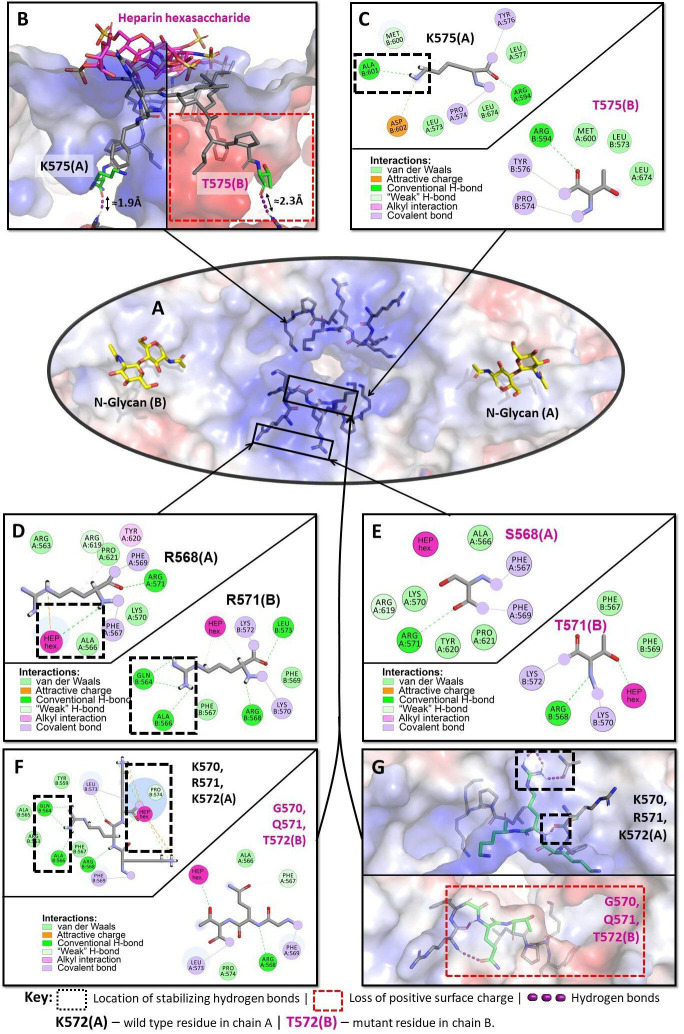
Figure 6. Structural analysis of the heparin-binding motif (HBM) in the 3D models for the R568S, R571T, and R568S/R571T mutants compared with the crystal structure of hDAO-WT.
(A) Top view of the HBM in hDAO-WT. R568 and R571 (green sticks) are the key residues in the positively charged HBM formed by arginines and lysines from both chains in the hDAO-WT dimer. Intramolecular interactions formed by R571 stabilize the HBM. (B) Top view of the HBM in hDAO-R568S dimer. The positively charged area is reduced around S568s in the R568S mutant compared to hDAO-WT (A). (C) Top view of the HBM in hDAO-R571T. The stabilizing interactions formed by R571 in hDAO-WT (A) are lost, and positive patches around T571s are reduced in hDAO-R571T. (D) Complex of hDAO-WT dimer with heparin hexasaccharide, sliced side view. R568s form hydrogen bonds with heparin hexasaccharide. (E) Complex of hDAO-R568S/R571T dimer with heparin hexasaccharide, sliced side view. In the R568S/R571T mutant, the positively charged surface patches and the stabilizing interactions are lost. Red color corresponds to the negatively charged surface, blue color indicates positively charged regions. hDAO: human diamine oxidase.