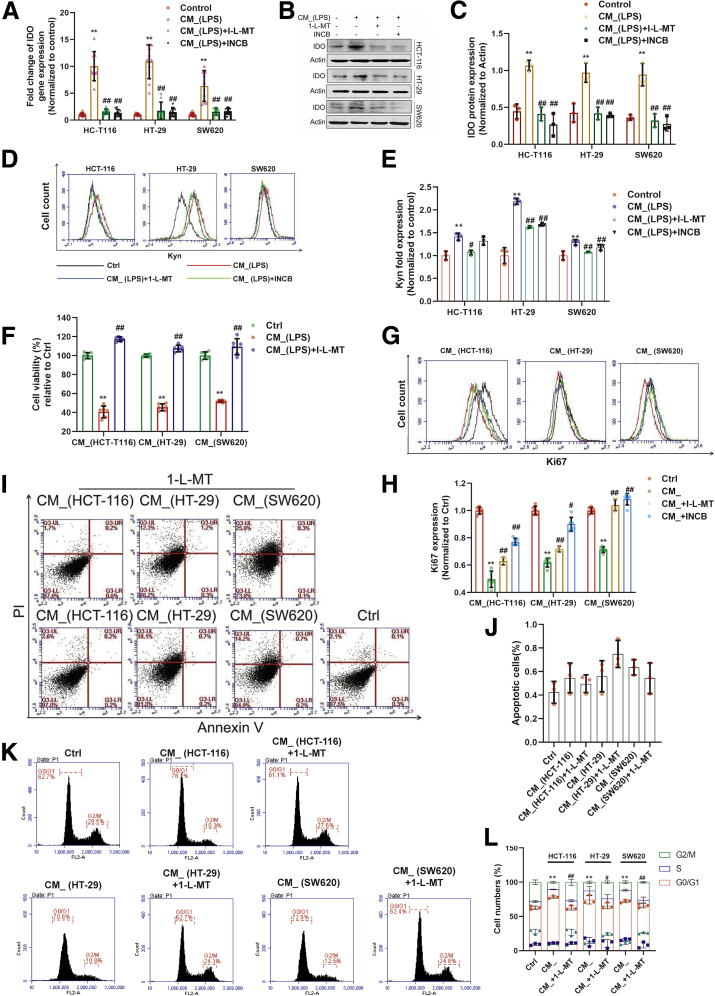
Figure 1.
IDO activation in colon cancer cells inhibited proliferation of activated T cells. (A–C) Lipopolysaccharide (2 μg/mL) stimulated THP-1 for 24 hours, and the supernatant was collected. (A) HCT-116, HT-29, and SW620 cells were incubated with such supernatant with or without the stimulation of 1-L-MT or INCB for 24 hours, and the gene of IDO expression was determined (n = 9). (B, C) The protein of IDO expression was determined by Western blot (n = 3). (D, E) The synthesis of Kyn was measured by flow cytometry. (F) The supernatant of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated THP-1 was incubated with HCT-116 (n = 3), HT-29 (n = 3), and SW620 (n = 3) cells with or without 1-L-MT or INCB for 24 hours, and then the supernatant (CM_) was collected. Jurkat cell lines (activated T cells) were stimulated with such CM_ for 24 hours. The cell viability was determined by CCK8. (G, H) Ki67 expression of Jurkat cells was detected by flow cytometry. (I, J) Activated T cells exposed to previous stimulation were analyzed for the extent of apoptosis by annexin V–tagged FITC-PI flow cytometry (n = 3). (K, L) Cell cycle distribution was measured using flow cytometry. The percentage of cells in each population are shown as the mean ± SD (n = 3). ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01 with control group. #P < .05, ##P < .01 with CM_ or CM_(lipopolysaccharide) group. The results were performed at least in triplicate and expressed as the mean ± SD. n.s, no significant difference.