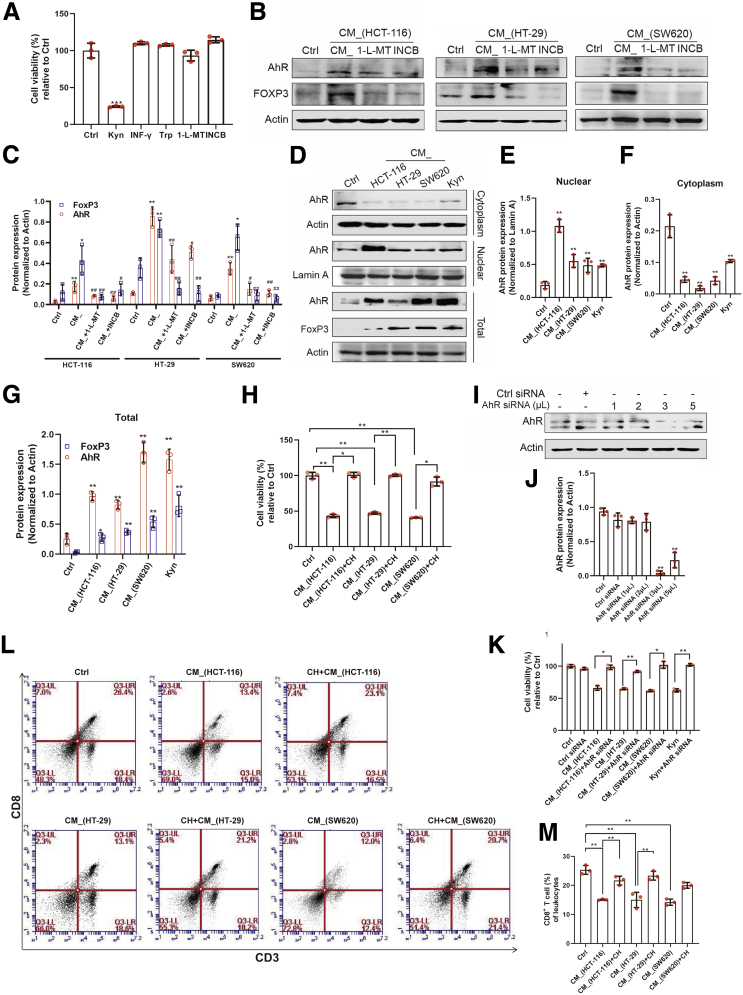
Figure 4.
Kyn/AhR was essential for IDO-mediated regulation of T cells. (A) Jurkat cells were exposed to the same dose (500 μM) of Kyn, INF-γ, Trp, 1-L-MT(1 mM), and INCB (10 μM) for 24 hours (n = 3). Cell viability was measured by CCK8. (B, C) The protein levels of AhR and FoxP3 in activated T cells after incubation with different CM_ were detected. (D–G) Jurkat cells were treated with CM_ or Kyn for 24 hours, and the protein level of AhR and its nuclear translocation were determined by Western blot (n = 3). (H) CM_-pretreated activated T cells were stimulated with CH-223191 (10 μM) for 24 hours, and cell viability was measured (n = 3). (I, J) Western blot analysis of AhR expression in Jurkat cells transfected with different concentrations of AhR siRNA for 24 hours. (K) AhR siRNA-transfected activated T cells were stimulated with CM_ for the indicated periods. Cell viability was determined by CCK8 (n = 3). (L, M) Mice spleen lymphocytes were cultured in the supernatant of colon cancer cells and CH-223191 (10 μM) for 24 hours. Percentage of CD3+CD8+ T cells was measured (n = 3). The results are representative of 3 independent experiments and are expressed as the mean ± SD. ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01 compared with the control, #P < .05, ##P < .01 compared with CM_ (A, C, E, F, G, and J). ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01 indicates significant difference (H, M).