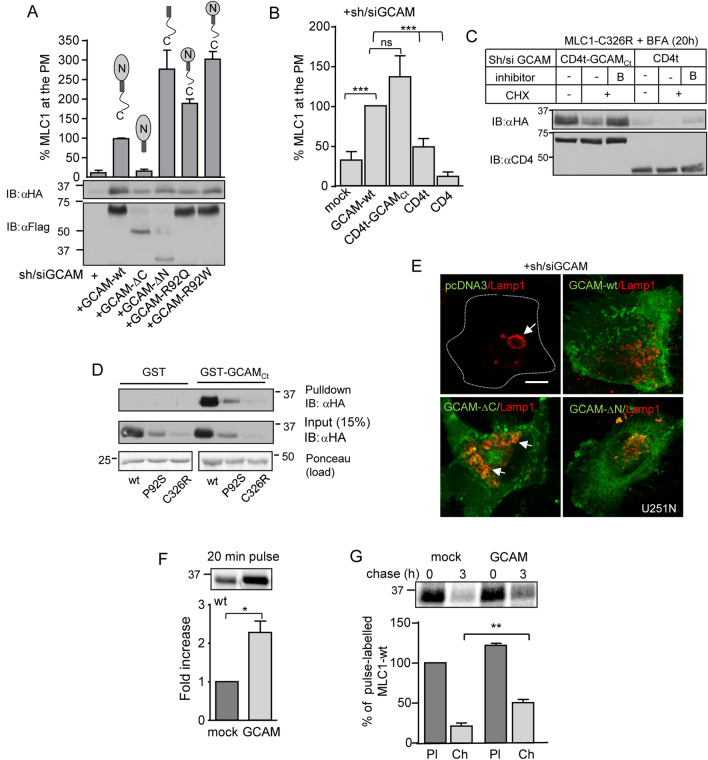
Figure 7.
GlialCAM is a chaperone-like folding assistant at the ER to enhance MLC1 biosynthetic secretion. (A) Structural requirements of GlialCAM (GCAM) for MLC1 trafficking to the PM. The PM density of MLC1 was measured using cs-ELISA in GCAM-depleted (si/sh) HeLa cells and expressing C- or N-terminally truncated GCAM-Flag variants as indicated. Western blot analysis is shown in lower panels. The C-terminal tail was minimally required to enable the PM targeting of MLC1. GCAM-R92Q or W are MLC disease-causing mutations. (B) The effect of the C-terminal tail of GCAM in trans on the PM expression of MLC1 was measured using cs-ELISA. Cells were depleted for GCAM (si/sh) and coexpressed with the C-terminal tail of GCAM fused to the truncated CD4, lacking its cytoplasmic tail (CD4t-GCAMCt). CD4t and CD4 were used as controls. (C) Western blot analysis of GCAMCt effect on the ER-retained MLC1 in the presence of BFA was performed as in panel (D), except using CD4t-GCAMCt coexpression and CD4t as a control. (D) Pulldown of MLC1 variants from cell lysates with the GST or GST fusion protein, containing the GCAMCt (GST-GCAMCt). (E) The effect of GCAM truncation on the endo-lysosomal pathway morphology was monitored in GCAM depleted (si/sh) astrocytic U251N cells. GCAM expression was detected with anti-GCAM and lysosomes with anti-Lamp1 Ab. Arrow points to enlarged Lamp1 + lysosomes. Bar 5 µm. (F) Phosphorimage analysis of metabolic pulse labelled (20 min, 37 °C) MLC1 with [35S] methionine/cysteine in +/− of GlialCAM overexpressing cells. (G) GlialCAM effect on the maturation of MLC1. Metabolic pulse-chase experiments as in panel (E), but using 1 h pulse-labelling at 26 °C and 3 h chase at 37 °C to allow the complete degradation of the ER-resident labelled MLC1 pool. Means ± SEM, n ≥ 3. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.