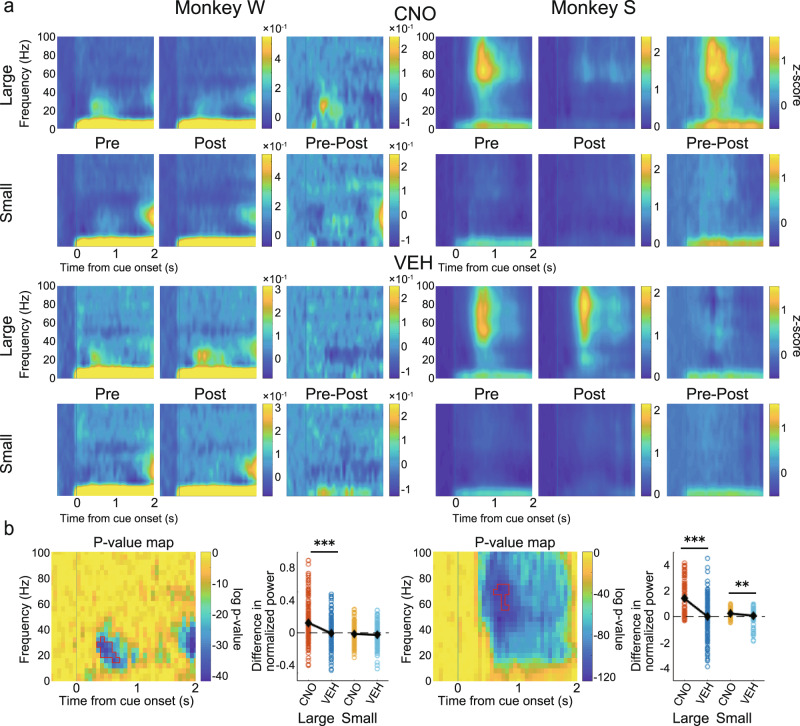
Fig. 4. Effects on spectrogram power in the LPFC after cue onset.
a Normalized and averaged spectrograms of LFPs from electrodes in the LPFC for Monkey W (Left) and Monkey S (Right), divided into large- and small-reward trials in the CNO (upper) and VEH (lower) condition. From left to right for each monkey, each spectrogram referred to Pre, Post, and their subtraction (Pre–Post). Color represents normalized power (−500 to 0 ms as baseline). Time 0 refers to the cue onset. b For each monkey: left: p-value map generated to extract time-frequency ROIs for statistical testing. Color represents log p-value obtained by comparing spectrograms in large- and small-reward trials. Areas surrounded by red lines indicate ROIs, which are the largest cluster among time-frequency data points having p-value in the bottom 5% (see “Methods”); right: comparison of the effects of CNO/VEH administration (Pre–Post) on normalized power averaged within ROIs divided into large- and small-reward trials. Each dot refers to the subtracted power from each electrode channel. Black diamonds represent mean values. CNO clozapine N-oxide, VEH vehicle, LFP local field potential, LPFC lateral prefrontal cortex, ROI region of interest.