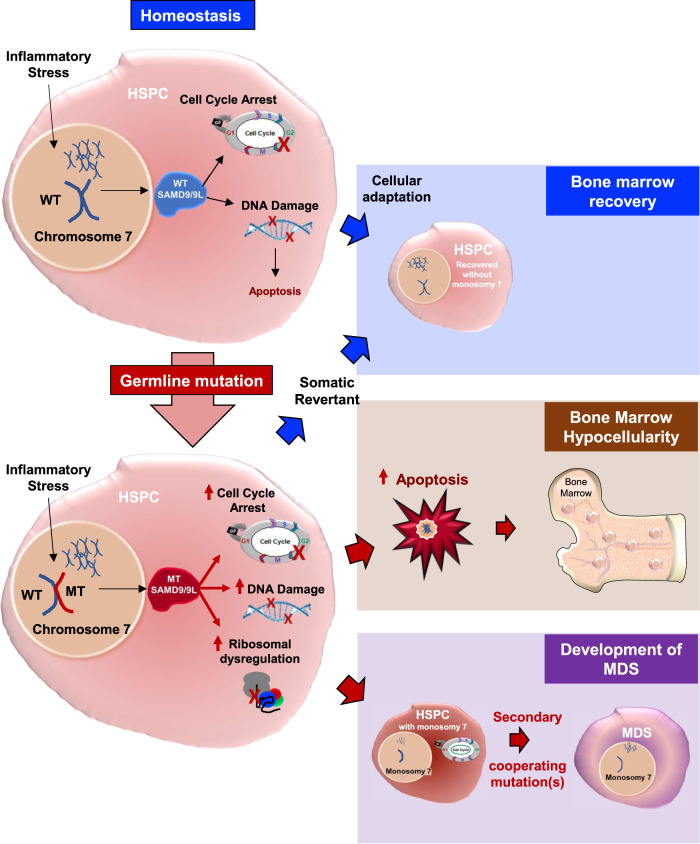
Fig. 6. Model of the functional roles of SAMD9 and SAMD9L in hematopoietic cells.
SAMD9 and SAMD9L regulate proteins involved in cell cycle, DNA damage repair, and protein synthesis. Mutated proteins (red) can significantly amplify these phenotypes, and if any of these remain unchecked, will ultimately lead to cell death. Collectively these features lead to bone marrow hypocellularity (middle). Alternatively, cells that lack the mutant protein (either by monosomy 7 or somatic reversion can have alternative fates dictated largely by the acquisition of additional somatic mutations. Hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell (HSPC), myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), wild-type (WT), mutant (MT).