FIGURE 2.
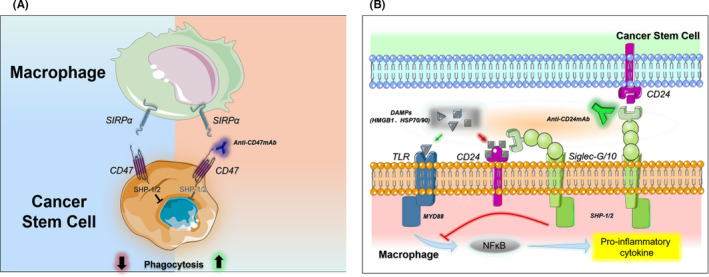
Antitumor mechanisms of CD47 and CD24 antibodies. (A) Anti‐CD47 antibodies promote macrophage phagocytosis of tumor cells by blocking the “don't eat me” signal. (B) CD24 antibody promotes tumor immune clearance and its potential adverse reactions. After blocking the highly expressed CD24 molecule on the surface of tumor stem cells, CD24 antibody prevents the activation of CD24‐Siglec‐g/10 signal, allowing macrophages to recognize tumor cells for immune clearance. In the inflammatory state, binding of TLR and DAMPs (such as HMGB1) activates the NFκB pathway, which ultimately leads to the release of pro‐inflammatory factors. The binding of CD24 and Siglec‐g/10 on the surface of macrophages to DAMPs through immune receptors tyrosine inhibitory motif (ITIM) signals blocks inflammatory process. In the presence of CD24 antibody, this inflammatory "braking" signal is seriously affected, leading to the emergence of cytokine storms. HGF/SF: hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor, MCP‐1: monocyte chemoattractant protein‐1, M‐CSF: macrophage colony‐stimulating factor, CL3CL1: fractalkine, CXCL, CCL: Chemokine Ligand, GD3: tumor‐derived ganglioside, iGb3: endogenous antigen, MICA/B (MHC class I chain‐related molecules A/B). DAMPS: damage associated molecular patterns, HMGB1: high mobility group box 1 protein, HSP: heat shock Proteins, TLR: toll‐like receptors, MYD88: myeloid differentiation factor 88
