FIGURE 6.
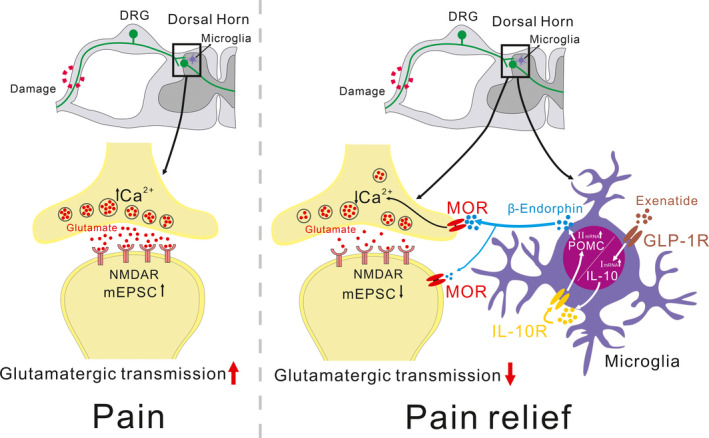
Schematic diagram showing the role of microglial expression of β‐endorphin in IL‐10‐ and specific GLP‐1 receptor agonist exenatide‐induced inhibition of spinal excitatory synaptic transmission and pain hypersensitivity in neuropathic pain. Following activation of GLP‐1 receptors, IL‐10 is released and then activates IL‐10 receptors via a microglial autocrine mechanism. Afterward, the β‐endorphin is released to microglial neuronal synapses and activates neuronal presynaptic and postsynaptic μ‐opioid receptors (MORs) to inhibit the enhanced glutamatergic transmission, leading to pain anti‐hypersensitivity
