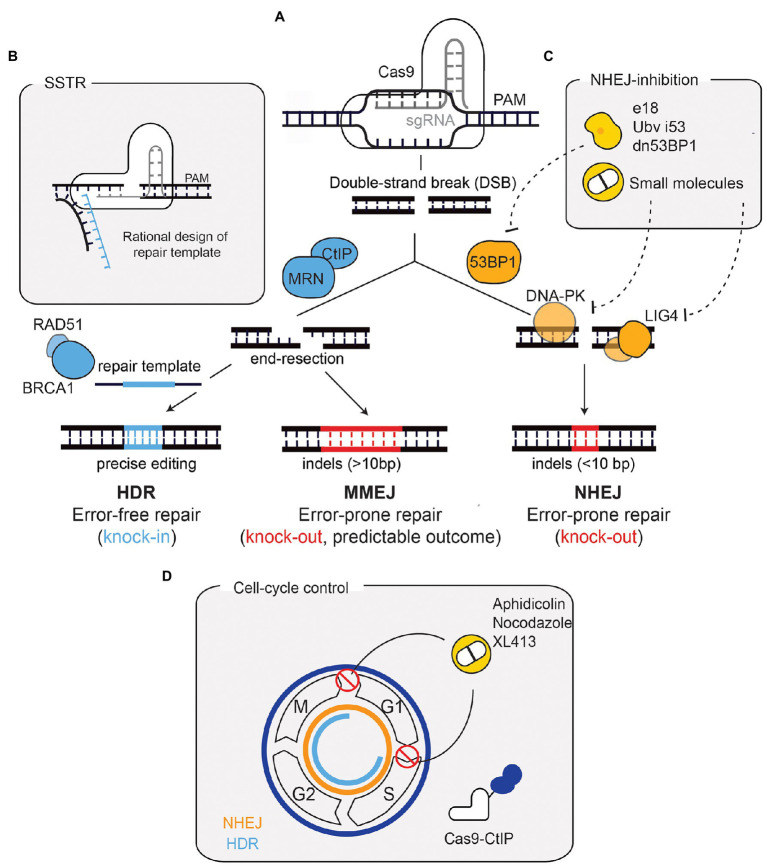
Figure 1.
Repair outcomes after a Cas9-induced DNA double-strand break (DSB) and strategies for enhancing precise repair. (A) Cas9, targeted by a sgRNA, induces a DSB in a precise region of the genome. Non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ), promoted by 53BP1, is the default repair pathway. Through the coordinated action of factors such as DNA-PK and LIG4, NHEJ repairs the DSB by re-joining the DNA-ends in an error-prone manner. This results in small insertions and deletions (indels) that can generate a loss-of-function allele if a frameshift is generated. If end-resection occurs [mediated by CtIP and MRE11-Rad50-NBS1 (MRN)], microhomology-mediated end-joining (MMEJ), or homology-directed repair (HDR) function. The repair outcome following MMEJ-mediated repair can vary, although this can be predicted since it depends on regions of microhomology and leads to larger indels. HDR, mediated by factors such as BRCA1 and RAD51, relies on a repair template and hence is error-free, leading to precise genomic alterations. (B) The use of ssDNA oligonucleotides (ssODN) as donor templates has also been developed to harness HDR. This process is called single-stranded templated repair (SSTR). SSTR is generally more efficient due to the asymmetry of the Cas9-DNA complex, which leads to the release of the PAM-distal non-target strand. Therefore, a rational design of the ssODN donor template complementary to the strand that is first released improves precise editing. (C) The inhibition of NHEJ has been used to improve precise repair following Cas9-breaks. 53BP1 inhibition through ubiquitin variants, dominant negative forms, or expression of factors that displace 53BP1, has proven useful. Small molecule inhibitors against DNA-PKcs and LIG4 have also been used. (D) Cell cycle manipulation has also proved useful for enhancing HDR. HDR (depicted in blue) is only active in S/G2/M phases, contrary to NHEJ (depicted in orange), which is active throughout the cell cycle. Strategies to improve HDR have included the use of compounds (such as XL413, aphidicolin, and nocodazole) to block cells in HDR-permissive phases. A Cas9-CtIP fusion allows end-resection (and subsequently HDR) to occur throughout the entire cell-cycle. PAM, protospacer adjacent-motif.