FIGURE 3.
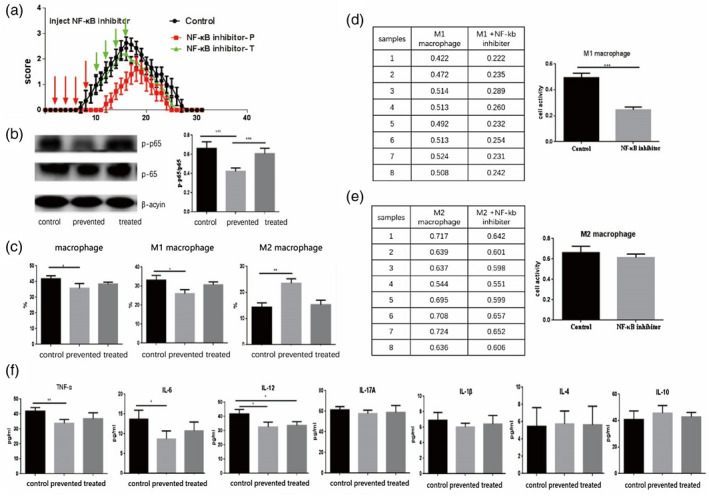
BAY11‐7082 treatment ameliorated the severity of experimental autoimmune neuritis (EAN). In a preventative treatment paradigm, BAY11‐7082 was administered from days 2 to 8 (20 mg/kg, once every 2 days) to EAN mice. The same dosage was applied in a therapeutic treatment paradigm from days 10 to 16. (a) EAN clinical scores were markedly better in BAY11‐7082‐preventative groups. The mice in the preventative group displayed notably better clinical scores from days 8 to 16 with the control group, but there no marked differences appeared for the clinical scores between the therapeutic and control groups. (b) BAY11‐7082 treatment inhibited production of p‐p65 in sciatic nerves of EAN mice. The BAY11‐7082‐preventative group had a significantly decreased expression of p‐p65 compared to BAY11‐7082 therapeutic and control groups. The expression of p‐p65 in the BAY11‐7082 therapeutic group was reduced when compared to the control group, but the differences were not significant. (c) The BAY11‐7082‐preventative group reduced the percentage of M1 macrophages and increased the number of M2 macrophages compared to the therapeutic and control groups. (d,e) BAY11‐7082 inhibited the proliferation of M1 macrophages, whereas the proliferation of M2, despite the differences, was not significant compared to control group in‐vitro studies. (f) The levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)‐α, interleukin (IL)‐12 and IL‐6 decreased greatly in the preventative treatment group compared to the control and therapeutic treatment groups. No marked differences appeared for the expression of IL‐17, IL‐1β, IL‐4 and IL‐10 among the three groups, but the levels of IL‐4 and IL‐10 increased although there was no significance
