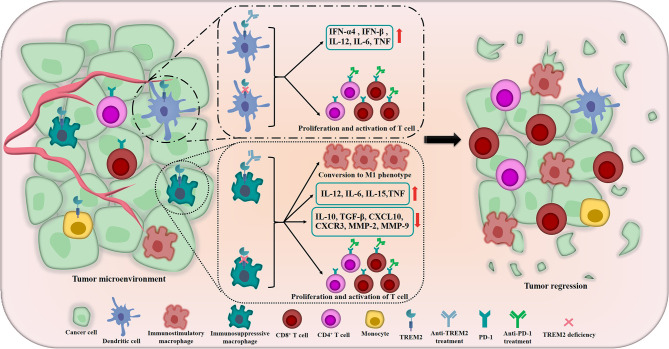
Figure 3.
The crucial roles of TREM2 in remodeling TME and inhibiting tumors. In TME, the tumor suppressor TREM2 is highly expressed in some myeloid cells including DCs, immunosuppressive macrophages, monocytes, etc. The inhibition of TREM2 could induce DCs produce increased type I IFN (including IFN-α4 and IFN-β), IL-12, IL-6 and TNF. In terms of regulating macrophages, TREM2 deficiency and anti-TREM2 mAb could promote the phenotypic conversion of macrophages to M1 phenotype which have anti-tumor function, meanwhile, the secretion of IL-12, IL-6, IL-15 and TNF are significantly induced and the levels of IL-10, TGF-β, CXCL10, CXCR3, MMP-2 and MMP-9 are decreased. More importantly, TREM2 deficiency and anti-TREM2 mAb also noteworthily promote the proliferation and activation of CD8+ T cells and CD4+ T cells which expressed PD-1 and potentially improve the responsiveness of cancers to anti-PD-1 treatments. The above crucial roles of TREM2 meaningfully remodel the TME and ultimately promote tumor regression and improve the therapeutic effect of immunotherapy.