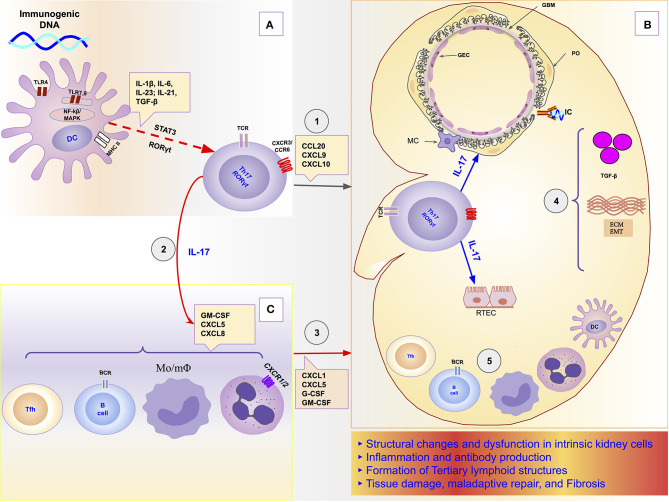
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the role of the Th17/IL-17 axis in the chain of events to kidney damage and ESRD in Lupus Nephritis. (A) Dendritic cells sense extracellular DNA through TLR4 present in their plasma membrane (69, 71, 72) or sense phagocyted DNA-containing immune complexes by TLR7 and TLR9 in endosome (69, 74, 75). The binding of DAMPs to TLRs in APCs induces their maturation (76, 77). Part of dendritic cells migrates to draining lymph nodes to present the processed antigen to T cells and induce their activation and differentiation. The differentiation of Th17 cells is promoted by proinflammatories cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, IL-21, IL-23) that dendritic cells secrete using the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways (77, 83). Dendritic cells that remained in the tissue secrete various chemokines like CXCL9, CXCL10, and CCL20 that drive the recruitment of Th17 cells to the kidney through binding to receptors (CXCR3 and CCR6) (96, 125, 126). (B) In the Kidney, Th17 releases its cytokines (IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-17C, IL-21, and IL-22) that act directly on intrinsic kidney cells (mesangial cells, podocytes; glomerular endothelial cells, renal tubular epithelial cells). IL-17 family cytokines are responsible for changes in the cytoskeleton of the podocytes, activation of inflammasome and caspases, and induction of oxidative stress and podocytes apoptosis. In addition, in tubular epithelial cells, IL-17 promotes the activation of the profibrotic pathways with the increase of the expression of TGF-β (36, 87), promotion of EMT (158) with consequent increase of extracellular matrix proteins and fibrosis (87). (C) Besides local effects, IL-17 amplifies the systemic inflammatory response by stimulating the synthesis of inflammatory cytokines, growth factors, and chemokines, resulting in granulopoiesis/myelopoiesis and recruitment of more immune cells to the kidney (31, 32, 194). In addition, it promotes autoantibody production by its effects on Tfh and GC (195, 196), and plasma cells (197). DC, dendritic cells; ECM, extracellular matrix; EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition; GBM, glomerular basement membrane; GEC, glomerular endothelial cells; IC, immune complex; IL-1, Interleukin-1; IL-17, Interleukin-17; IL-21, Interleukin-21; IL-23, Interleukin-23; IL-6, Interleukin-6; MAPK, Mitogen-activated protein kinase; MC, mesangial cell; Mo/mΦ, Monocytes/macrophages; NF-κB, Nuclear factor-κ B; PO, podocyte; RTEC, renal tubular epithelial cells; Tfh, follicular helper T cells; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-beta; Th17, T helper lymphocytes, subtype 17; TLR2, Toll-like receptor 2; TLR4, Toll-like receptor 4.