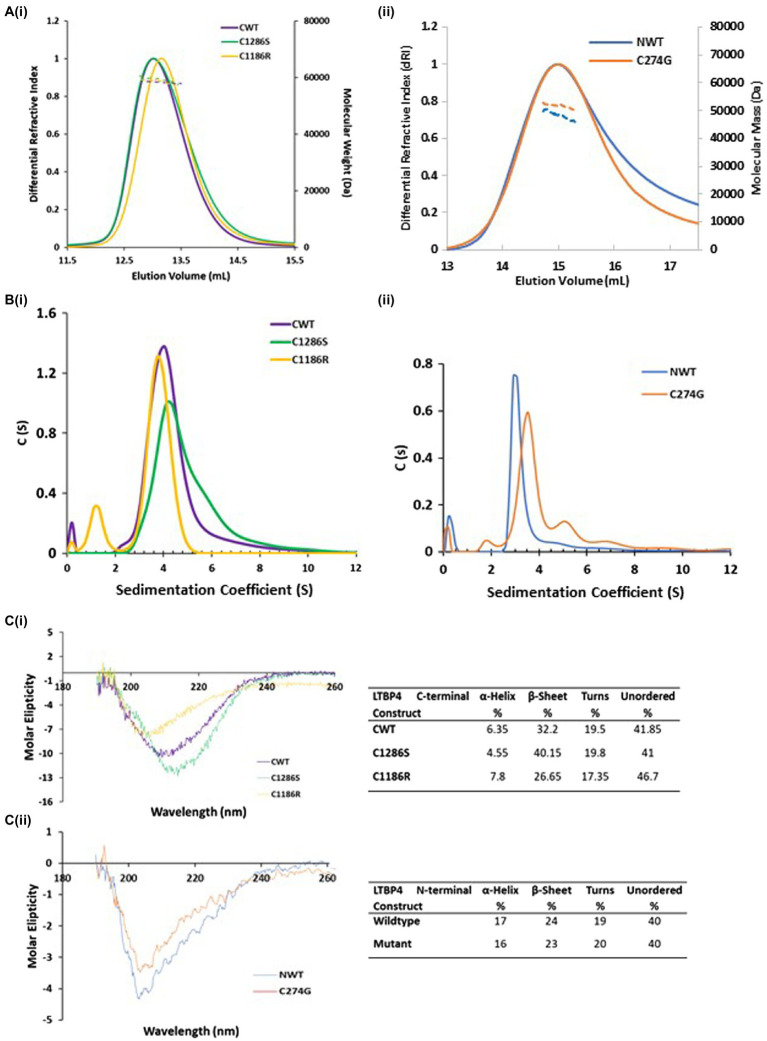
Figure 2.
Hydrodynamic properties and secondary structural characterisation of LTBP4. (A) SEC-MALS chromatograms in which the differential refractive index (solid lines) and molecular weight (dashed lines) are plotted as a function of elution volume (ml). The colours are purple (CWT), gold (C1186R), green (C1286S), blue (NWT) and orange (C274G) and this colour scheme is used in all figures. All constructs are monomeric in solution with mass of 58 kDa for the LTBP4 C-terminal constructs (i), and 47 and 51 kDa for the NWT and C274G constructs (ii), respectively. (B) Sedimentation velocity profiles from AUC for the (i) C-terminal and (ii) N-terminal LTBP4 constructs. (C) The far-UV-CD spectra in the 260–190 nm range for the wild type and mutant LTBP4 (i) C-terminal and (ii) N-terminal constructs. CD data show that the spectra have a negative maxima characteristic of proteins with a high β-sheet content and unordered conformation. The C1286S substitution had little impact on the CD spectra, whereas a more pronounced difference was observed for C1186R. Ten scans were recorded for each sample. The table summarises the secondary structure content of the wild-type and mutant constructs.