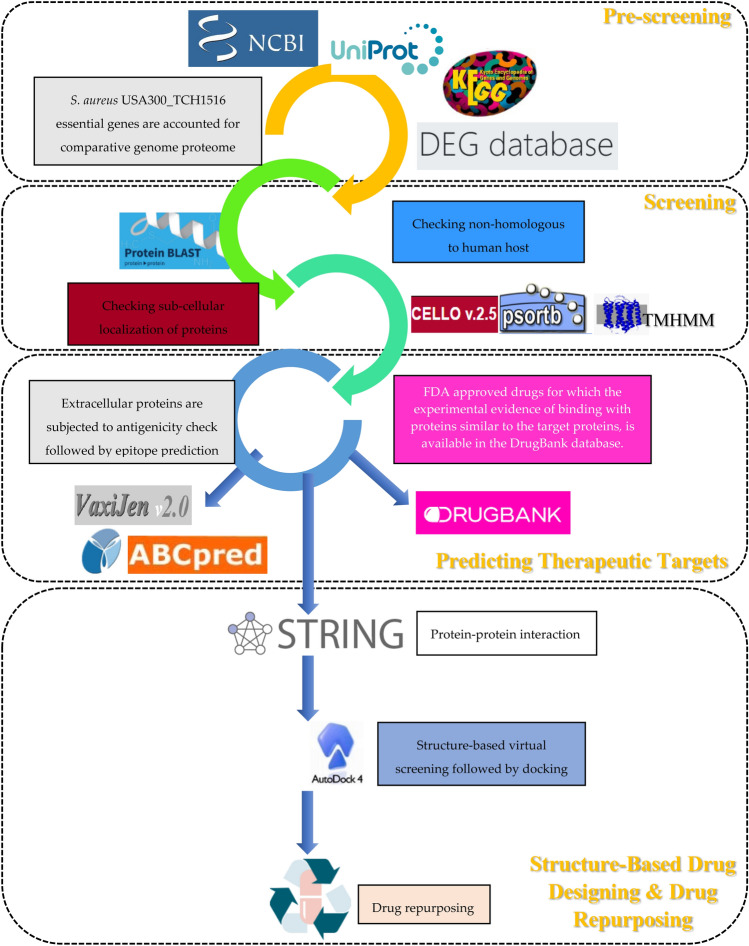
Fig. 1.
The schematic workflow of subtractive genome proteome analysis for predicting potential therapeutic targets for Staphylococcus aureus USA300. This study involves four steps, including Pre-screening, where genome, proteome data of S. aureus USA300_TCH1516 was retrieved from various databases followed by Screening. Bacterial essential proteins are checked for non-homologous to the human host, and sub-cellular localization analysis was performed in the Screening step. In the next step, B-cell epitopes were predicted for the extracellular proteins, and drug targets are identified from the pool of bacterial essential non-homologous proteins by searching in the DrugBank database for which the experimental evidence of binding with proteins similar to the target proteins are available. The final step involves the Structure-based drug designing and drug repurposing approach for an essential non-homologous protein selected based on protein–protein interaction analysis