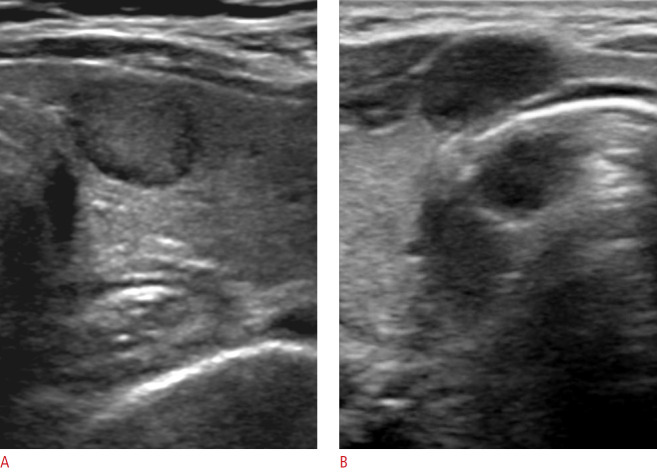
Fig. 2. Modified K-TIRADS 4A nodule with a solid hypoechoic US pattern in a 66-year-old woman (A) and modified K-TIRADS 4B nodule in a 29-year-old woman (B).
A. Transverse US shows a solid and mildly hypoechoic nodule (12 mm) without any suspicious US features (microcalcification, spiculated or microlobulated margin, or nonparallel orientation) and macrocalcification in the right thyroid lobe. This nodule is classified as intermediate-risk by the AACE/ACE/AME guideline, moderately suspicious (TR4) by the ACR TI-RADS, intermediate suspicion by the ATA guideline, intermediate-risk (TIRADS 4) by the EU-TIRADS, and intermediate suspicion (TIRADS 4) by the K-TIRADS. Final diagnosis: nodular hyperplasia by surgery. B. Transverse US shows a solid and markedly hypoechoic nodule (11 mm) without any suspicious US features and macrocalcification at the isthmus of thyroid. This nodule is classified as high-risk by the AACE/ACE/AME guideline, moderately suspicious (TR4) by ACR TI-RADS, intermediate suspicion by the ATA guideline, high-risk (TIRADS 5) by the EU-TIRADS, and intermediate suspicion (TIRADS 4) by the K-TIRADS. Final diagnosis: papillary thyroid carcinoma by surgery. K-TIRADS, Korean Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System; US, ultrasonography; AACE, American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists; ACE, American College of Endocrinology; AME, Associazione Medici Endocrinologi; ACR TI-RADS, American College of Radiology Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System; ATA, American Thyroid Association; EU-TIRADS, European Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System.