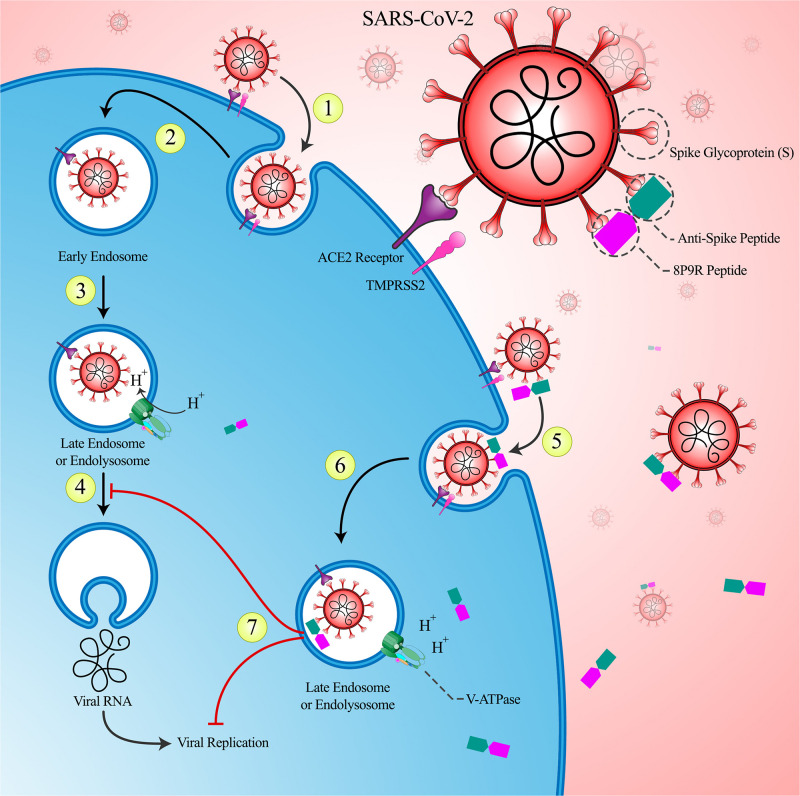
FIGURE 1.
The role of intervention in the primary phase of the COVID-19: (1) The SARS-CoV-2 virus enters the host cell via angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptors with the help of TMPRSS-2. (2) Following the complete entrance of the virus, the early endosome forms. (3) The environment of the early endosome becomes acidic, as it matures and turns into late endosome. This acidification is caused by inward flow of protons through V-ATPase channels. (4) The acidification of endosome helps the virus to escape to the cytoplasm and move on with its replication. (5) The designed chimeric 8P9R peptide is able to attach to the spike protein of the virus. This attachment can prevent the viral ligand (spike protein) from bonding to its receptor and therefore neutralizes the virus. Thereafter, this peptide would internalize alongside with the virus to help the host cell to battle against the virus with the help of its inherent antiviral characteristics. (6) This peptide has a strong positive charge that interferes with the inward flow of protons and attenuates the acidic environment of endosome and thus prevents the viral escape. (7) Not only this peptide is able to prevent viral escape via attenuated endosomal acidification, but also it can directly interfere with viral replication and therefore decrease the viral load.