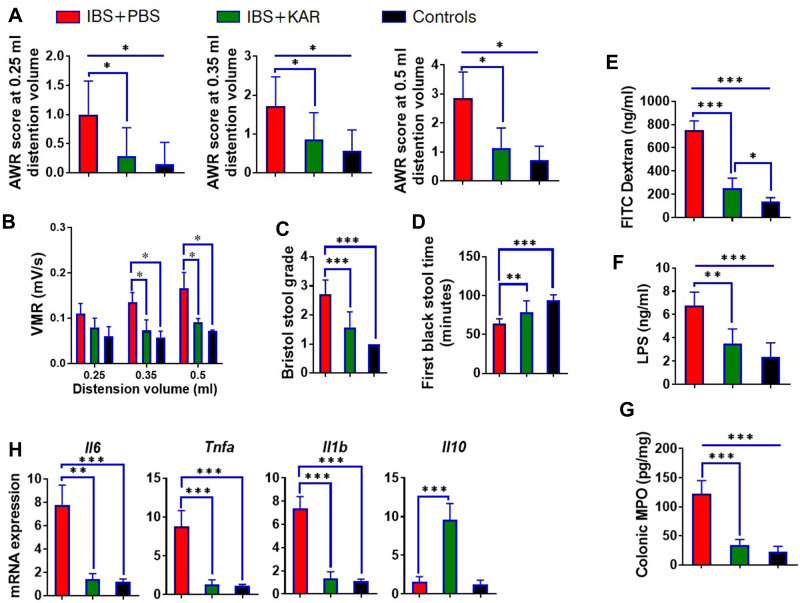
Figure 1.
Kurarinone (KAR) alleviates visceral hypersensitivity and inflammatory responses in mice with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). An IBS mouse model was established as indicated. IBS mice (wild type on a C57BL/B6J background) were daily received intraperitoneally with PBS or KAR (> 99% purity, WuXi PharmaTech, Shanghai, China) at the dosage of 100 mg/kg/day beginning from 10 days post TNBS insults to the end of the experiment. Age- and gender-matched wild type (WT) mice that were not exposed to 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid (TNBS) served as the control group. (A) The abdominal withdrawal reflex (AWR) test was performed to evaluate the visceral hypersensitivity in response to colorectal distention (CRD) in mice at distending volume of 0.25, 0.35, or 0.5 mL. (B) Kinetic visceromotor response (VMR) to CRD at distending volume of 0.25, 0.35, or 0.5 mL. (C) Bristol stool grade. (D) The first black stool time. Intestinal permeability was mirrored by serum (E) FITC-dextran and (F) LPS concentrations. (G) The level of MPO in the colon was measured to represent the activity of neutrophils. (H) The transcript expression levels of colonic IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-10 were measured by qRT-PCR. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). n = 8 mice in each group. Representative results from one of three independent experiments were shown.