Fig. 10.
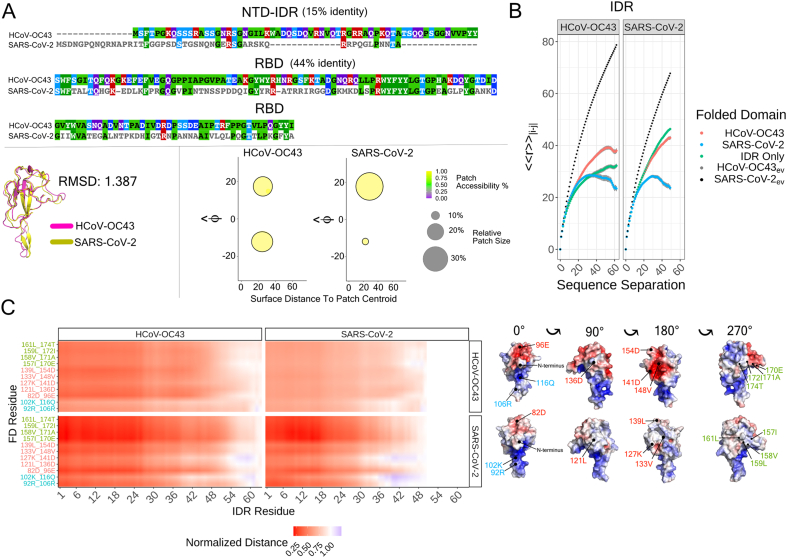
The RBD of OC43 and CoV-2 N protein influences IDR conformational behavior and IDR-FD interactions. A) Aligned sequences of OC43 and CoV-2 N protein (top), aligned structures of OC43RBD and CoV-2RBD (bottom-left), and patch information for OC43RBD and CoV-2RBD (bottom-right). B) Internal scaling profiles for each tail (OC43NTD or CoV-2NTD) attached to each RBD (OC43RBD and CoV-2RBD) and each tail in isolation for the full Hamiltonian simulations. The black dotted line represents the internal scaling profile for the corresponding IDR-FD excluded volume simulations. C) Scaling maps for each of the four proteins; OC43NTD-OC43RBD (top-left), OC43NTD-CoV-2RBD (bottom-left), CoV-2NTD-OC43RBD (top-right), CoV-2NTD-CoV-2RBD (bottom-right). Each entry in the scaling map refers to the average distance between residues i and j in the full Hamiltonian simulation divided by the average distance between residues i and j in the corresponding excluded volume simulation. Inter-residue distances were calculated between all residues of a given tail and 11 specific residues on each RBD. Because there is not an exact one-to-one mapping between the linear sequence and their geometric location for the two RBDs, we determined an isomorphic mapping between 11 specific residues (e.g residue 92 [R] for CoV-2RBD corresponds to residue 106 [R] for OC43RBD, etc.). To the right of the scaling map, we show these residues in context of the electrostatic surface potential maps for OC43RBD and CoV-2RBD.