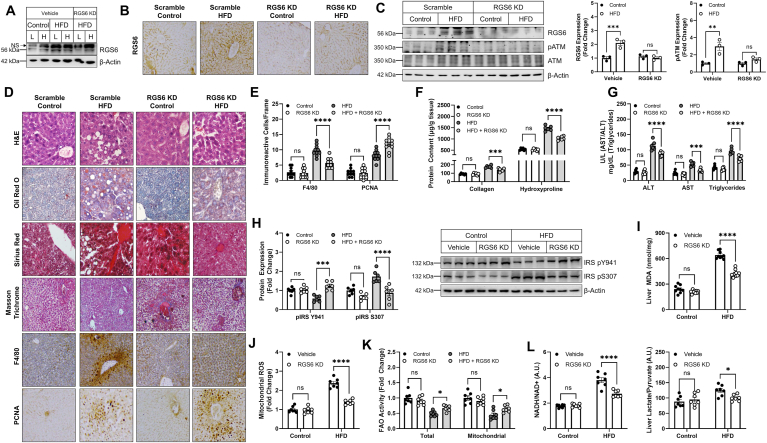
Fig. 4.
RGS6 KD in liver protects against hepatosteatosis and fibrosis in HFD-fed mice. Control and HFD (54.8% total fat content)-fed mice were administered scramble or RGS6-targeted shRNA via tail vein injection prior to initiation of the HFD (n = 6). Animals were sacrificed after 12 weeks of HFD feeding. (A) Immunoblotting for RGS6 in liver [L] and heart [H]. (B) Hepatic RGS6 expression measured via immunohistochemistry [scale bar = 100 μm]. (C) Immunblotting for RGS6, pATM and ATM with densitometric quantification. (D) Histological characterization of livers. Liver architecture (H & E), fibrosis (Masson Trichrome, Sirius Red), inflammation (F4/80), regeneration (PCNA) and lipid accumulation (Oil Red O) are depicted [scale bar = 100 μm]. (E) F4/80 and PCNA positive cells per microscope field (n = 10). (F) Hepatic collagen and hydroxyproline content (n = 6/group). (G) Liver enzyme (ALT & AST) and triglyceride levels. (H) Immunoblotting for markers of insulin sensitivity with corresponding densitometric quantification. (I) Liver MDA (n = 7). (J) Mitochondrial ROS (Mitosox) generation (n = 7). (K) Total and mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation (FAO) rate in liver (n = 7). (L) Liver metabolism as indicated by NADH/NAD+ and Liver Lactate/Liver pyruvate (n = 7). β-Actin is used as a loading control for all immunoblots. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA with Sidak's post-hoc test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01,***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)