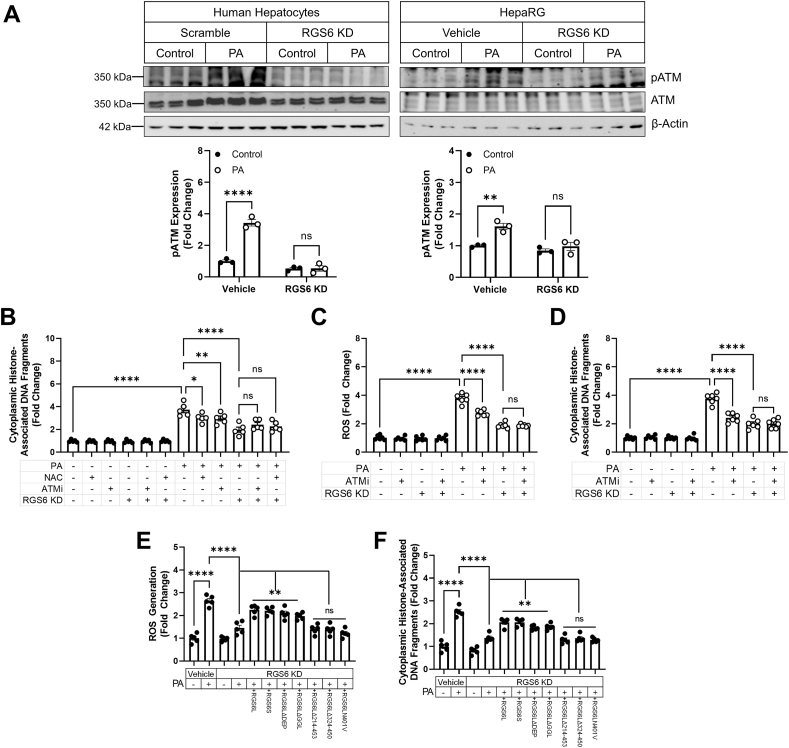
Fig. 7.
RGS6, ATM and ROS function in the same pathway to promote hyperlipidemia-dependent hepatotoxicity. Scramble or RGS6-targeted shRNA was introduced into human hepatocytes (A, B) or HepaRG cells (A, C–F) 24 h prior to treatment with PA (400 μM, 24 h), NAC (5 mM, 1 h pre-treatment) and/or the ATM inhibitor KU55933 (ATMi; 5 μM, 1 h pre-treatment) where indicated. In a subset of experiments RGS6 deletion constructs were introduced via transfection prior to drug treatments. (A) Immunoblotting for pATM and ATM. Representative westerns and a densitometric quantification are provided (n = 3). β-Actin is used as a loading control for all immunoblots. (B) Cell death (cytoplasmic histone-associated DNA fragments; n = 5) ± RGS6 KD, ATMi, and/or NAC in human hepatocytes. (C) CM-H2DCFDA fluorescence (n = 6) and (D) cell death (cytoplasmic histone-associated DNA fragments; n = 6) ± RGS6 KD and/or ATMi. (E) CM-H2DCFDA fluorescence (n = 5); (F) cell death (cytoplasmic histone-associated DNA fragments; n = 6); and albumin production (n = 5) ± RGS6 KD and/or RGS6 deletion constructs. Data were analyzed by one- or two-way ANOVA with Sidak's post-hoc test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001. ns = not significant. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.