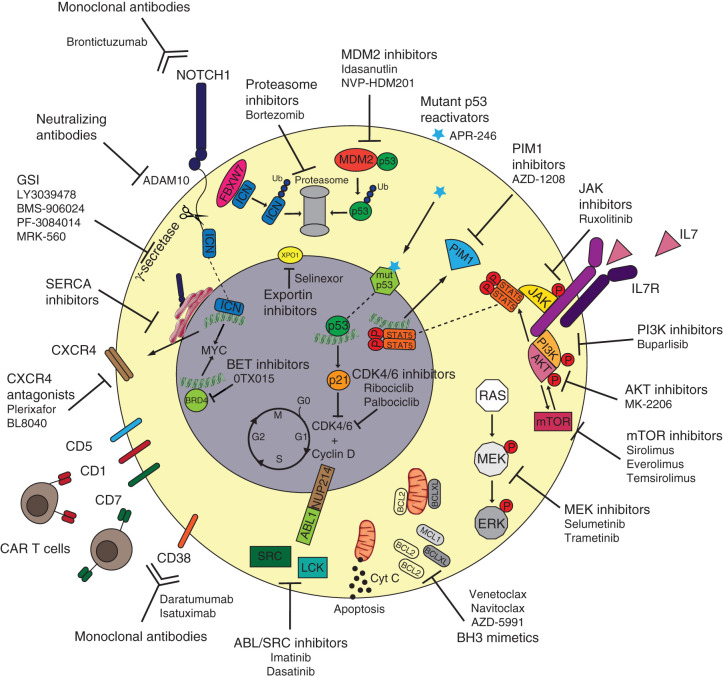
Figure 1.
Targeted therapies to tackle T-ALL vulnerabilities. Oncogenic NOTCH1 signaling can be inhibited via different strategies such as monoclonal antibodies blocking the NOTCH1 receptor itself (brontictuzumab), monoclonal antibodies blocking the ADAM10 metalloprotease that releases extracellular NOTCH1, gamma-secretase inhibitors (GSI) preventing the release of intracellular ICN1, and SERCA inhibitors that block the maturation of NOTCH1 and its localization on the cell surface. Because NOTCH1-mutated T-ALL cases can present higher CXCR4 surface expression, CXCR4 antagonists (plerixafor and BL8040) can be used to tackle NOTCH1-driven T-ALL as well. Immunotherapy approaches for T-ALL include monoclonal antibodies against surface CD38 (daratumumab or isatuximab) as well as CAR T cells directed toward surface CD1, CD5, CD7, and CD38. The increased expression of antiapoptotic BH3 proteins such as BCL2 and BCLXL can be counteracted by the use of BH3 mimetics (venetoclax, navitoclax, and AZD-5991). The oncogenic signaling of ABL1 fusion proteins as well as aberrant activity of Src-family kinases can be inhibited by the tyrosine kinase inhibitors imatinib and dasatinib. The aberrant IL7R signaling cascade can be tackled using multiple targeted agents including JAK inhibitors (ruxolitinib), PIM1 inhibitors (AZD-1208), PI3K inhibitors (buparlisib), AKT inhibitors (MK-2206), mTOR inhibitors (sirolimus, everolimus, or temsirolimus), and MEK inhibitors (selumetinib or trametinib). APR-246 can bind mutant p53 and restore its wild-type, tumor-suppressor function, whereas MDM2 inhibitors (idasanutlin and NVP-HDM201) can prevent wild-type p53 ubiquitination and consequent degradation via the proteasome. Alternatively, tumor-suppressor proteins' degradation can be prevented by proteasome inhibitors (bortezomib). Increased activity of cell-cycle regulators CDK4/6 can be blocked by CDK inhibitors (ribociclib or palbociclib), whereas aberrant transcription induced by BRD4 can be targeted by BET inhibitors (OTX015). Nuclear trafficking of oncogenic mRNA and proteins can be targeted via XPO1 inhibitors (selinexor).