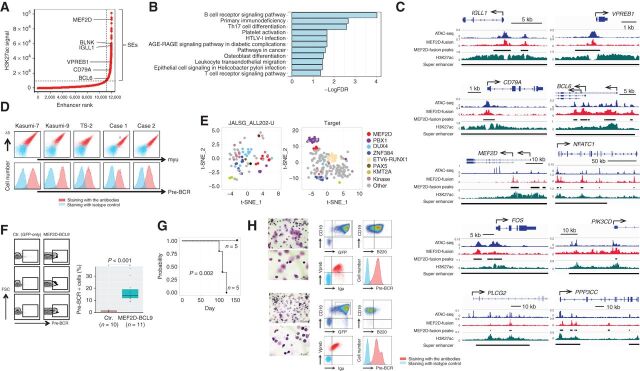
Figure 1.
Association of MEF2D-fusion with pre-BCR expression. A, Profile of enhancers in Kasumi-7 cells based on the H3K27ac ChIP-seq signal. Enhancers are ranked by increasing signal level. SEs are represented in the top right quadrant. Genes assigned to selected SEs are indicated. B, KEGG pathway analysis of the genes assigned to SEs involving MEF2D-HNRNPUL1 occupancy. The false discovery rate (FDR) is indicated. C, Occupancy of MEF2D-HNRNPUL1 in genomic regions near the transcription start sites of representative genes involved in pre-BCR signaling. ATAC-seq and H3K27ac ChIP-seq signals are indicated. The MEF2D-HNRNPUL1 signal peaks and SEs are indicated by black lines. The x and y axes indicate the linear sequences of genomic DNA and normalized read densities, respectively. Arrows indicate the locations and directions of the TSSs. D, Flow cytometric analysis of pre-BCR expression on the indicated cells. Cells were labeled using a combination of anti-Igμ and anti-λ5 antibodies (top) and an anti-pre-BCR complex antibody (bottom). E, t-SNE analysis of genes associated with pre-BCR–positive versus -negative BCP ALL in clinical samples from two independent cohorts. Each dot represents one sample. The colors of the dots indicate fusions involving the indicated genes. “Kinase” indicates genes associated with protein kinases. F, Association of enforced MEF2D-BCL9 expression with pre-BCR+ B-cell emergence in mice. Mice were transplanted with mouse pro-B cells infected with retroviruses encoding GFP-only (n = 10) or MEF2D-BCL9 plus GFP (n = 11). Pre-BCR expression in the GFP+ fraction was analyzed by flow cytometry 3 weeks after transplantation. Representative flow-cytometric plots (left) and the % pre-BCR+ cells among total GFP+ cells (right) demonstrate the association of MEF2D-BCL9 expression with the emergence of pre-BCR+ B cells. G, Kaplan–Meier curves of estimated survival among mice transplanted with control (n = 5) and MEF2D-BCL9-expressing pro-B cells (n = 5). This cohort was independent of that described in F. The statistically significant difference in survival was determined using the log-rank test. H, Morphologic (May–Grunwald–Giemsa staining) and flow-cytometric analyses of bone marrow cells of two mice before death revealed many lymphoblasts positive for pre-BCR.