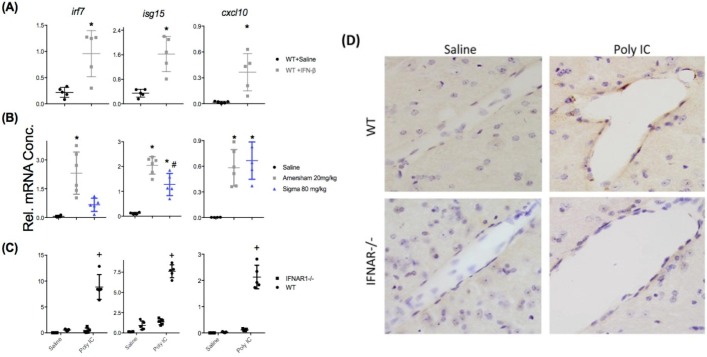
Fig. 5.
Relationship between circulating IFNβ and brain interferon-dependent responses. A) Hippocampal expression of interferon-dependent genes in adult female C57BL/6 mice treated with IFN-β (25,000 units i.p.; 3hr post injection) challenge compared to WT Saline treated (n = 5 per group; unpaired Student’s t-test, ** p < 0.01). (B) Comparison of C57BL/6 mice challenged with saline, HMW (20 mg/kg) or LMW (80 mg/kg) poly I:C at 5hr post injection (n = 4,6,5 for saline, HMW and LMW respectively; one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-hoc analyses: * indicates p < 0.05 when compared to saline and # indicates p < 0.05 when comparing both poly IC treatments). (C) Comparison of poly IC (HMW 20 mg/kg), 3 hrs post injection) in C57BL/6 mice and IFNAR1-/- mice (all groups n = 5 except WT saline n = 4; + denotes significant difference between IFNAR1-/- poly IC and WT poly IC and also between IFNAR1-/- poly I:C and IFNAR1-/- saline (p < 0.05) (D) Representative bright field photomicrographs (40X) of CXCL10 immunohistochemistry showing CXCL10-positive cells at the vascular endothelium, present only in WT poly I:C group.