Figure 5. Nitrate regulates PIN2 phosphorylation levels.
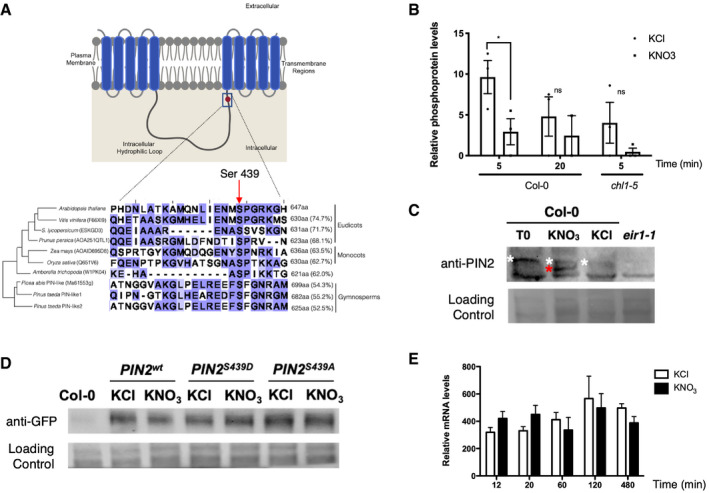
- Schematic representation of the phosphosite (Ser439) identified in PIN2 in our study. PIN2 protein possesses three specific regions: a region with five transmembrane segments (residues 1–163), a central hydrophilic loop extending from residue 164 to 482 and a region with five additional transmembrane segments (residues 483–647). Protein alignment with PIN2 or PIN‐like proteins from different species indicates conservation of the serine residue in eudicot, monocot, and gymnosperm species. The red arrow highlights the S439 in the central loop of PIN2 proteins in different plants. The size of each protein in amino acids and the percentage of identity against the Arabidopsis PIN2 are indicated.
- Levels of PIN2 phosphopeptide in our experiments. Bars represent the mean plus standard error of replicates (2 biological replicates for nitrate treatments at 20 min (Col‐0 roots) and 3 biological replicates for all other experimental conditions). Each independent biological replicate consisted of a pool of 4.500 roots collected from Arabidopsis plants grown independently under the same experimental conditions. The asterisk indicates statistically significant differences in phosphoproteomic analysis (multiple t‐test comparison without testing corrections, assuming same variance, P < 0.05).
- Detection of phosphorylation PIN2 by Phos‐tag Western blotting. Arabidopsis plants (Col‐0) were growth in ammonium as only nitrogen source and treated with 5 mM KNO3 or 5mM KCl as control. Total protein from roots were analyzed in SDS–PAGE using Phos‐tag to detect changes in phosphorylation status. Immunoblotting was performed with PIN2 antibody. Total proteins isolated from eir1.1 roots were used as a negative control. White and red asterisks indicate a slow‐ or fast‐mobility band corresponding to a more or less phosphorylated PIN2, respectively.
- Western blot against PIN2 protein comparing nitrate‐treated (KNO3) and control (KCl) condition in Arabidopsis roots for all genotypes eir1‐1 mutant background was complemented with PIN2::PIN2wt‐GFP (PIN2wt), PIN2::PIN2S439D‐GFP (PIN2S439D phospho‐mimic point mutation), or PIN2::PIN2S439A‐GFP (PIN2S439A, phospho‐null point mutation).
- Time‐course analysis of PIN2 mRNA levels in response to nitrate treatments in Arabidopsis roots. Bars represent the mean plus standard deviation of 3 biological replicates.
Source data are available online for this figure.
