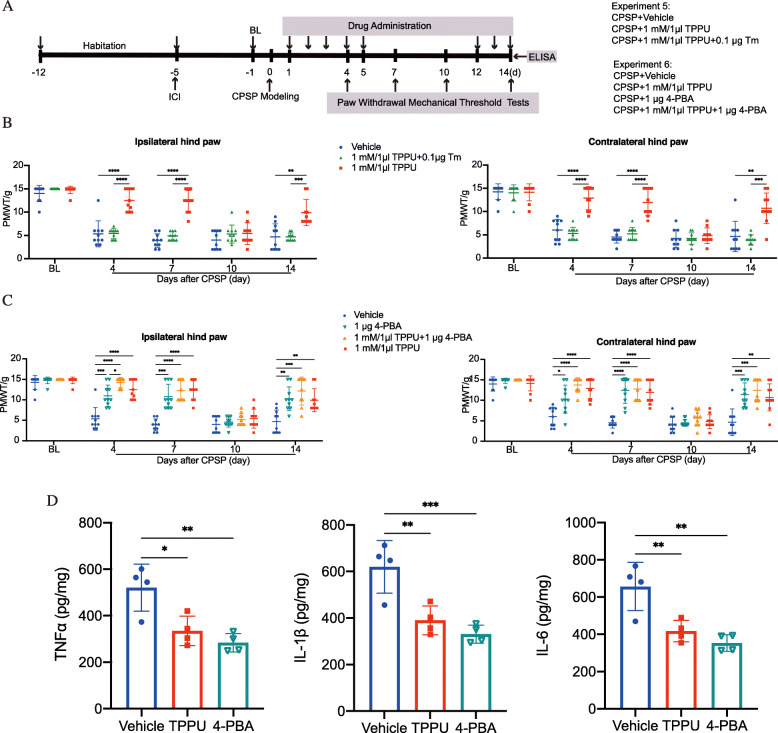
Fig. 7.
The ER stress inducer Tm abolished the analgesic effect of TPPU in the CPSP rats. a The timeline of the present experiment. b Application of the ER stress inducer Tm (0.1 μg) completely reversed the analgesic effect of TPPU (1 mM/1 μl) in both hind paws under CPSP conditions during the postlesional 14-day observation period. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, n = 10 per group, two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni tests. c Administration with ER stress inhibitor 4-PBA alone induced a marked suppression of mechanical allodynia in both hind paws in CPSP rats. However, treating CPSP rats with a combination of 4-PBA and TPPU did not result in further attenuation of mechanical allodynia, as no difference was found among the TPPU, 4-PBA, and TPPU + 4-PBA groups. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001compared with vehicle group, n = 10 per group, two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni tests. d Either TPPU (1 mM/1 μl) or 4-PBA (1 μg) reduced the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines including TNFα, IL-1β, and IL-6 around the perilesion site of the thalamus at day 14 after CPSP induction. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, compared with vehicle-treated CPSP group, n = 4 per group, one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni tests