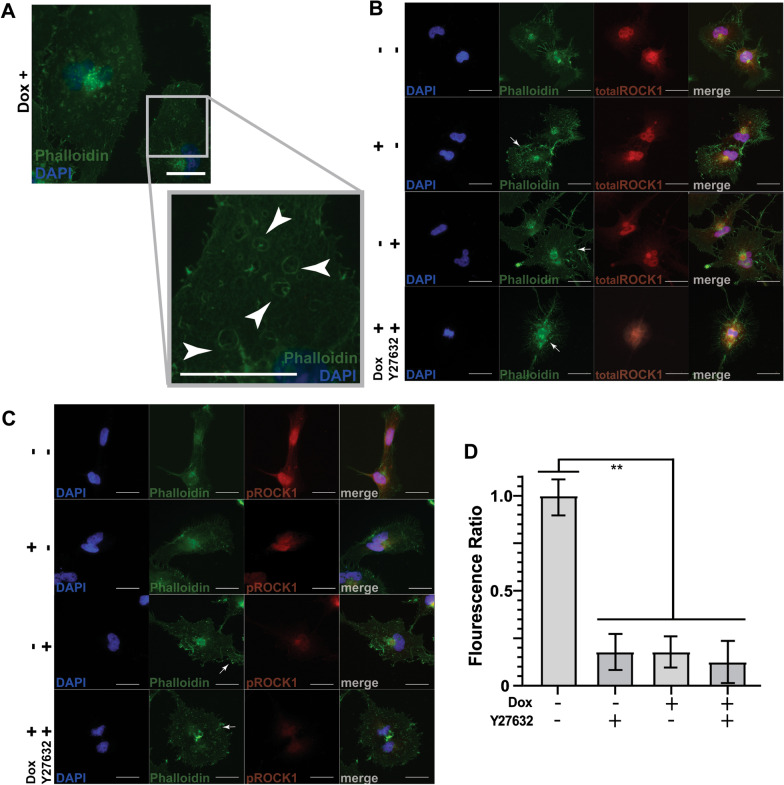
Fig. 6.
DN R-Ras decreases phosphorylation of ROCK1 and alters migration and cell morphology. a Effect of DN R-Ras expression on the actin cytoskeleton in ST88-14 cells as assessed by phalloidin staining. The enlarged image demonstrates actin-rimmed vesicular structures (white arrows) that accumulate in ST88-14 cells following induction of DN R-Ras expression. b, c Total ROCK1 (b; red) or phospho-ROCK1 immunoreactivity (c; red) in ST88-14 MPNST cells in the presence (+) or absence (−) of DN R-Ras expression and treatment with vehicle (−) or the ROCK inhibitor Y27632 (+). Cells were counterstained with phalloidin counterstain (green) to demonstrate cell morphology as highlighted by the actin cytoskeleton and bisbenzimide (blue) to label nuclei. Arrows denote notable changes in the actin cytoskeleton, including a loss of filamentous structures and the accumulation of actin-rich puncta (white arrows) following induction of DN R-Ras expression or Y27632 treatment. A non-immune isotype matched primary antibody was used as a negative control. Scale bars = 25 μm. d Semi-quantitative analysis of normalized total and phosphorylated ROCK1 levels relative to uninduced or untreated controls. **, p-value < 0.0001