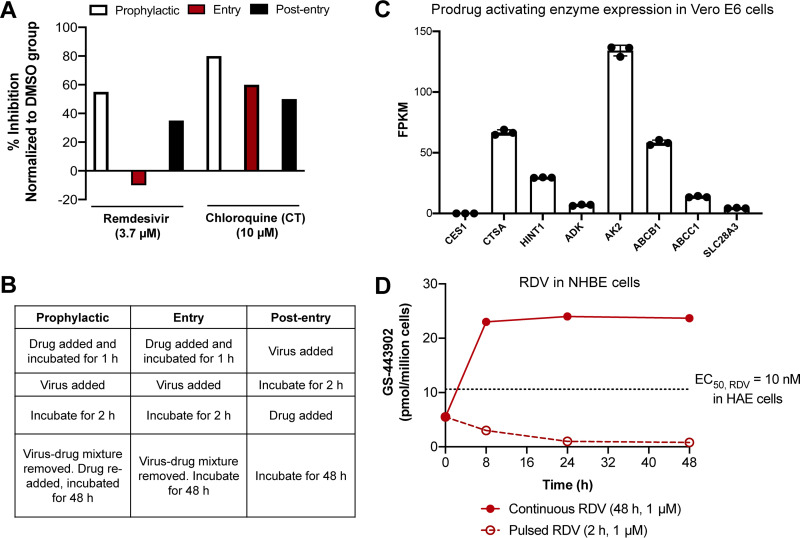
FIG 2.
Duration of drug exposure impacts the antiviral efficacy of remdesivir. (A) Continuous exposure to RDV leads to durable in vitro inhibition of SARS-CoV-2, but pulsed treatment with RDV results in diminished antiviral activity in Vero E6 cells. Data are means of triplicate data replotted from reference 29. Across the three experiments, RDV was tested at 3.7 μM and CQ was tested at 10 μM. Due to its long in vivo t1/2, CQ serves as a positive control. (B) Corresponding treatment procedures for prophylactic, entry, and postentry experiments described for panel A. Pulsed experiments correspond to the entry trial. (C) Transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq) data showing expression of relevant prodrug bioactivating enzymes for RDV in Vero E6 cells, presented as means and standard deviations (SD) from 3 experiments (see the supplemental material). ADK, adenosine kinase; AK2, adenylate kinase 2. AK2 and SLC29A3 were found to mediate RDV potency and toxicity in a genome-wide CRISPR screen (55). (D) Formation of active triphosphate (GS-443902) in normal human bronchial epithelial (NHBE) cells following pulsed (open circles) and continuous (filled circles) incubation. Data are adapted from reference 36 and are presented as means for at least 2 independent replicates. The dotted line at 10.6 pmol/million cells corresponds to the mean C24 of triphosphate formed by RDV in SARS-CoV-2-infected HAE cells when the EC50 was determined to be 10 nM, as reported in reference 5.